Recently, Hyundai Motor Group released a video showing the history of its crash safety technology. The video demonstrated the history of Hyundai Motor Group’s crash safety technology for the EV platforms and the 3rd generation platforms, which have been widely used even before the era of platforms. It also informs that the Hyundai Motor Group not only responds to the safety standards of the new vehicle evaluation program, which are getting more strict day by day, but also shows that their ultimate goal is to establish a mobility safety system without any casualties.
Basics for building a vehicle: crash safety

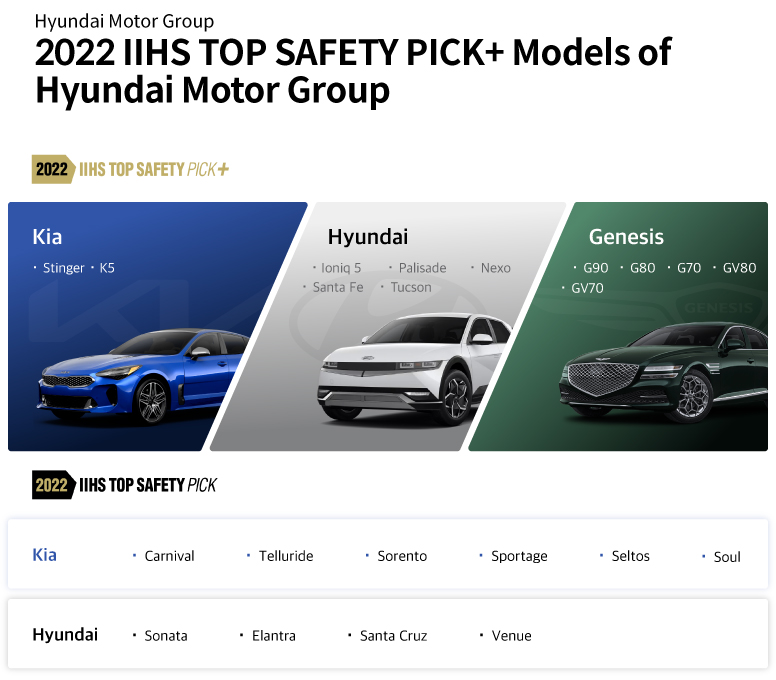
Hyundai Motor Group earned the most’ Top Safety Pick (TSP)’ and ‘Top Safety Pick+ (TSP+)’ in the new car crash safety evaluation conducted by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) this year. IIHS’s crash tests not only show strict standards but also encourage manufacturers to make safer cars by updating test features based on the current trend of traffic accidents. IIHS in the North American market is so influential that it is considered one of the most strict standards for automobile safety.

Obviously, today’s passenger safety doesn’t just mean design‒based crash safety; As active driving convenience and safety features such as ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System) are getting popular, crash safety evaluation agencies are also considering ADAS as well as headlamps in their evaluation criteria to prevent accidents. Ironically, however, the design is becoming more thorough for passenger protection in the event of a crash because crash safety is now considered the basis of passenger safety.
As such, for the basics of passenger safety, Hyundai Motor Group has continued its efforts for decades of vehicle technology development and passenger safety to become the safest manufacturer ‒ the 3rd generation platform that most Hyundai Motor Group models currently house, for example. E‒GMP, developed for the EV era, is also a platform that reflects passenger safety‒oriented design.
Evolution of Hyundai Motor Group’s design for safety

The body, which is the main structure of an automobile, is largely divided into a crumple zone and a safety zone in terms of crash safety. The crumple zone absorbs the impact energy from the outside. As the engine is gradually downsized and the space‒maximizing cab‒forward body becomes mainstream; and the front crumple zone naturally decreases as the engine room shrinks. In line with these design trends, automakers have been developing cars in a way that absorbs collision energy as much as possible, even in a compact space.
On the other hand, the safety zone is where passengers board, as shown in the picture. Therefore, by improving the rigidity of each part as much as possible, they are designed to maintain their original shape as much as possible, even a collision occurs from any direction.

The establishment of the platform of Hyundai Motor Group and the detailed evolution leading to the 3rd generation platform were completed in accordance with this basic safety design concept. Its very first platform began with the first Genesis unveiled by Hyundai Motor Group in 2008. The 5th‒generation Avante and the 6th‒generation Sonata also have this concept, and the first‒generation platform increased the efficiency of first energy absorption in the event of a frontal collision by improving the strength of the front back beam and front side members.
In addition, the first‒generation platform utilized the *Tailor Welded Blanks (TWB) structure that induces sequential energy absorption in the front side members, its dash cross members were added, and the strength of the center pillars and side sills was also improved. In particular, the safety zone was further secured by actively utilizing the hot stamping method, which innovatively enhances the strength of the steel plate. This is a crucial difference between the first‒generation platform and the current one.
*TWB (Tailor Welded Blanks): A welding method that cuts and integrates plates of different materials and thicknesses

Genesis (codename BH), which was based on the 1st generation platform, had proven its high crash safety by acquiring TSP, which was the highest safety grade of IIHS at the time (TSP+ rating system was newly established in 2013), as soon as it was released in the North American market. . And its second‒generation platform reflected the IIHS and other agencies’ requests for safety improvements in partial frontal crashes. For example, by connecting the parts that make up the *load path on the front more firmly and raising the strength at the same time, the impact was more effectively distributed. In addition, the ultra‒high tensile strength ratio was increased by 51% to secure the safety of collisions occurring from the front, side, and rear, and the rigidity of the body was improved by expanding the use of structural adhesives to 110m.
*Load path refers to how vehicle loads are transferred down through a structure

The second‒generation platform does not stop at responding to small overlap tests. A new technology was introduced to enhance the protection of the safety zone. This technology consists of steel plates with different strengths in different parts of each center‒pillar panel; The lower part, which has relatively low strength, is designed to absorb the impact energy by deforming during a collision, and the part with high strength is designed to support the load and dissipate the impact energy.
Proving the safety performance of the new platform, Hyundai Motor Group obtained the highest grade of ‘G (Good)’ in the small overlap test in the first year of the small overlap test, and also received excellent grades in other tests. . Since the IIHS, the small overlap test has been used in KNCAP hosted by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of the Republic of Korea and the EU’s EURO NCAP. Since then, as more and more models housed Hyundai Motor Group’s second‒generation platform, more of them earned the highest rating.
3rd Generation Platform: A Complete Platform in the Age of Internal Combustion Engines

Since the establishment of the era of the platform, Hyundai Motor Group has been steadily reinforcing core structures necessary for safety by gradually applying body design technologies that have been difficult to use until now. And through the technology they have built up based on decades of experience in platform production, they started to produce the 3rd generation platform. The 3rd‒generation platform, unveiled in 2019 along with the 8th‒generation Sonata, is a complete platform in the era of internal combustion engines that satisfies the incompatible elements ‒ improved crash safety and dramatic weight reduction.

One of the key points of the 3rd generation platform is load path optimization. Hyundai Motor Group has completed a ‘multiple skeletal structure’, adding a front structure to its second‒generation platform and changing the member composition. It is designed to spread the impact energy generated in a frontal collision more widely. In addition, in order to protect the fuel tank or the battery of an electrified vehicle in the event of a rear‒end collision, the crash load was minimized by using a load path setting that distributes the strength of the side members.

In addition, they improved the strength of the overall frame, including the roof rail and front back beam, and expanded the hot stamping method to the front and center pillars, side sills, and dash lower parts to increase the strength of the entire frame to an average of 71 kgf/mm² (about 700 MPa). In addition, the weight has been reduced through new lightweight materials. In fact, the body weight of Genesis’ 3rd generation G80 is up to 125kg lighter than its predecessor.
In addition, Hyundai Motor Group also introduced an innovative design to prevent secondary accidents on the 3rd generation platform. This “behavior control technology” assumed a partial frontal collision like the small overlap test. By partially disengaging the wheels of the collision part to the outside of the body, the vehicle is pushed sideways and prevents a large turn. This lowers the possibility of passenger injury and prevents secondary accidents at the same time.

As such, Hyundai Motor Group has evolved through its platform. For example, the hot stamping method was used in a wider range as the platform passed through generations. In the 3rd generation platform, most of the frames forming the safety zone are made of ultra‒high‒strength steel plates that have undergone a hot stamping method. In addition, structural adhesives were used more to maximize passenger protection performance.
After the load path concept was introduced in the 1st generation platform, the completion of the multi‒path load path over the 2nd and 3rd generations is the core of evolution. By distributing the impact energy applied toward the car body more widely, the shock absorption performance of the crumple zone could be greatly improved. Hyundai Motor Group’s platform design based on its basics safety design has been reflected in the Electric‒Global Modular Platform (E‒GMP), an EV‒dedicated platform, and is expected to work effectively in the near future.
Designing E‒GMP structures for safer electrified vehicles

In December 2020, Hyundai Motor Group first unveiled ‘E‒GMP’, a platform dedicated to electric vehicles for the era of eco‒friendly mobility. E‒GMP is not only equipped with innovative features such as the world’s first 400V / 800V multi‒quick charging system and bi‒directional V2L, but also boasts safety, which is the basis of an automobile platform.

First of all, Hyundai Motor Group added a special design and structure unique to E‒GMP to comply with the characteristics of EV batteries. This design is primarily to protect passengers as well as minimize the impact on the battery. Using a clever design that utilizes the battery pack as a structure, aluminum extrusions were used for the side sills outside the battery from the side of the body while increasing the rigidity of the body. This configuration secures safety by distributing impact to the lower frame and battery case in case of a side collision.
In addition, E‒GMP has an 8‒point fastening structure in which 8 bolts penetrate the battery pack so that the body and battery are integrated. In addition, in case of a rear‒end collision, the deformation of the rear member is intentionally generated to absorb the impact to prevent damage to the battery, while the lower member is reinforced with a hot‒stamped steel plate to prevent deformation of the safety zone. In addition, this is designed to perfectly deal with all kinds of collisions that may occur during driving by adding a battery case with a lattice structure and a lower protective cover.
And E‒GMP houses the core structure of the 3rd generation platform. The main load path was changed to the side sill and the A‒pillar part according to the layout after installing the battery. In addition, when the whole energy caused by the collision is concentrated on the partially front part ‒ as in the small overlap test ‒, a multi‒skeletal structure consisting of the double box member disperses the energy.

On the other hand, statistically, side collision is known as the second most frequent traffic accident next to a frontal collision. Hyundai Motor Group thoroughly considered this side collision in designing E‒GMP. For example, the cross member connecting the left and right side members was expanded to improve rigidity, and aluminum reinforcement was added to the battery case. This unique platform structure protected the battery and the occupants even in an intense side collision.

As the E‒GMP’s seamless safety design shows, Hyundai Motor Group’s all‒electric vehicles achieve the highest ratings in new car safety evaluations in major countries; For example, the Hyundai IONIQ 5 earned the highest grade ‘Top Safety Pick+ (TSP+)’ in the IIHS crash safety evaluation last July. In addition, the Genesis GV60 proved its outstanding safety of E‒GMP in both domestic and overseas markets, as it obtained the highest rating of five stars in EURO NCAP and TSP+ in IIHS in September and November.

The history of occupant safety accumulated by Hyundai Motor Group for decades contains numerous efforts. In addition, the Hyundai Motor Group boasts preemptive technologies such as the development of the world’s first airbag technology. The automaker has become a trendsetter that changes the paradigm of automobile safety through its Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) regardless of class. Until autonomous driving vehicle becomes a reality, Hyundai Motor Group will pour its heart into collision safety in every direction.