Lear’s (NYSE:LEA) stock is up by 2.8% over the past month. We wonder if and what role the company’s financials play in that price change as a company’s long-term fundamentals usually dictate market outcomes. Specifically, we decided to study Lear’s ROE in this article.
Return on equity or ROE is an important factor to be considered by a shareholder because it tells them how effectively their capital is being reinvested. In simpler terms, it measures the profitability of a company in relation to shareholder’s equity.
View our latest analysis for Lear
How To Calculate Return On Equity?
Return on equity can be calculated by using the formula:
Return on Equity = Net Profit (from continuing operations) ÷ Shareholders’ Equity
So, based on the above formula, the ROE for Lear is:
13% = US$646m ÷ US$5.1b (Based on the trailing twelve months to December 2023).
The ‘return’ is the yearly profit. One way to conceptualize this is that for each $1 of shareholders’ capital it has, the company made $0.13 in profit.
What Is The Relationship Between ROE And Earnings Growth?
We have already established that ROE serves as an efficient profit-generating gauge for a company’s future earnings. Depending on how much of these profits the company reinvests or “retains”, and how effectively it does so, we are then able to assess a company’s earnings growth potential. Assuming everything else remains unchanged, the higher the ROE and profit retention, the higher the growth rate of a company compared to companies that don’t necessarily bear these characteristics.
A Side By Side comparison of Lear’s Earnings Growth And 13% ROE
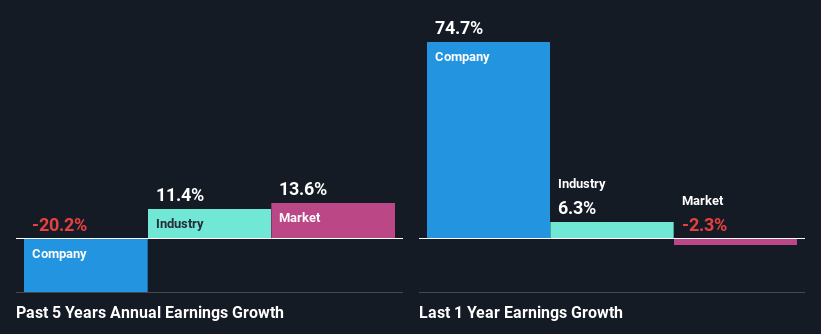
To start with, Lear’s ROE looks acceptable. Even when compared to the industry average of 11% the company’s ROE looks quite decent. However, while Lear has a pretty respectable ROE, its five year net income decline rate was 20% . We reckon that there could be some other factors at play here that are preventing the company’s growth. For example, it could be that the company has a high payout ratio or the business has allocated capital poorly, for instance.
However, when we compared Lear’s growth with the industry we found that while the company’s earnings have been shrinking, the industry has seen an earnings growth of 11% in the same period. This is quite worrisome.
Earnings growth is a huge factor in stock valuation. The investor should try to establish if the expected growth or decline in earnings, whichever the case may be, is priced in. By doing so, they will have an idea if the stock is headed into clear blue waters or if swampy waters await. Has the market priced in the future outlook for LEA? You can find out in our latest intrinsic value infographic research report.
Is Lear Using Its Retained Earnings Effectively?
Despite having a normal three-year median payout ratio of 35% (where it is retaining 65% of its profits), Lear has seen a decline in earnings as we saw above. So there could be some other explanations in that regard. For instance, the company’s business may be deteriorating.
Moreover, Lear has been paying dividends for at least ten years or more suggesting that management must have perceived that the shareholders prefer dividends over earnings growth. Our latest analyst data shows that the future payout ratio of the company is expected to drop to 16% over the next three years. The fact that the company’s ROE is expected to rise to 18% over the same period is explained by the drop in the payout ratio.
Conclusion
In total, it does look like Lear has some positive aspects to its business. However, given the high ROE and high profit retention, we would expect the company to be delivering strong earnings growth, but that isn’t the case here. This suggests that there might be some external threat to the business, that’s hampering its growth. Having said that, looking at current analyst estimates, we found that the company’s earnings growth rate is expected to see a huge improvement. Are these analysts expectations based on the broad expectations for the industry, or on the company’s fundamentals? Click here to be taken to our analyst’s forecasts page for the company.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.