Osaka, Japan – Panasonic Corporation announced today that it has commercialized a high vibration acceleration-resistant (50 G or higher), surface-mounted type power choke coil [1] (10 mm square size) suitable for power circuits in automotive electronic control units (ECUs) employed in hybrid electric vehicles, electric vehicles, and gasoline-powered vehicles. The company will launch the new product by the end of this month.
With the growing demand for energy efficiency of eco-friendly cars and the need to comply with environmental regulations, computerization of cars has been rapidly expanding, and ECUs are being incorporated more frequently and on larger scales in cars. In addition, more ECUs are being placed within the engine itself, elevating integration of mechanical and electronic in-vehicle components [2]. This trend has created a need for automotive ECUs that can be installed in high-temperature environments that have more severe vibration conditions and support large current. Choke coils with high resistance to vibration and heat as well as support for large current are essential for removing noise and smoothing the power supply of power circuits that constitute automotive ECUs. The company is launching its surface-mounted type power choke coil for automotive use achieving the industry’s highest(*1) resistivity of 50 G or higher vibration acceleration.
Panasonic’s new power choke coil has the following features:
- The industry’s highest*1 resistance to vibration acceleration, enabling the automotive ECU to be more resistant to vibration
• The newly developed power choke coil withstands vibration acceleration of 50 G or higher in 150ºC environments (490 m/s²). The conventional product*2 only withstands vibration acceleration of 15 G (147 m/s²). - Remove the need for the anti-vibration reinforcement as part of the board mounting process, allowing the streamlining of the production process.
• It reduces the use of reinforcing measures with bonding agents (adhesives). - Its excellent heat-resistance and support for large current contributes to the ability to place automotive ECUs in the engine itself.
• Current value: 27 A, Heat resistance: 150°C/2,000 h, equivalent to conventional product*2
- *1: As a surface-mounted type power choke coil for automotive use (10 mm square size) as of April 17, 2018 (Panasonic data)
- *2: Panasonic’s conventional product: 10 mm square size power choke coil for automotive use (PCC-M1050ML series)
Suitable applications:
DC/DC converter circuits [3] and power circuits for high-performance ECUs incorporated in hybrid electric vehicles, electric vehicles, and gasoline-powered vehicles, and mechanical-electrical-integrated automotive ECU circuits
[Product Features]
1. The power choke coil has the industry’s highest resistance to vibration acceleration, enabling automotive ECUs to be more resistant to vibration
The placement of automotive ECUs has been changing from the engine compartment to the engine itself, which requires coils used in automotive ECUs to have high resistance to vibration. Conventional products structurally have a low self-resonant frequency [4] around 2,000 Hz and have an issue with vibration resistance. By utilizing the company’s metal composite material [5] using its unique metal magnetic material and own winding and molding technologies, Panasonic created a coil with a high self-resonant frequency of 3,000 Hz or higher leading to the industry’s highest resistance to vibration acceleration of 50 G or higher, contributing to more vibration-resistant automotive ECUs.
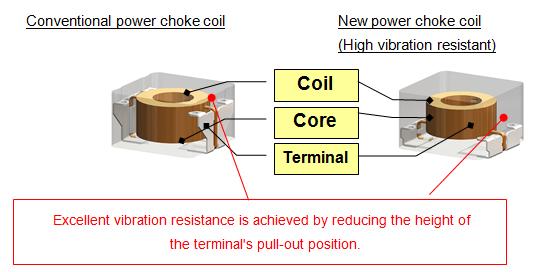
2. The new power choke coil removes the need for anti-vibration reinforcement as part of the board mounting process, allowing the streamlining of the production process
The conventional automotive ECU board mounting process requires anti-vibration measures, such as anchoring components with bonding agents (adhesives), to make the ECU resistant to vibration. The height of the developed power choke coil’s terminal pull-out position is reduced to half that of the company’s conventional product through the adoption of the company’s unique winding and molding technologies, allowing its placement near the mounting board to achieve excellent vibration resistance. This has made conventional anti-vibration measures unnecessary, allowing the streamlining of the production process.

3. The power choke coil, with excellent heat-resistance and support for large current, contributes to the placement of automotive ECUs within the engine itself
Coils used in automotive ECUs are required to be heat-resistant and support high current, in addition to being highly resistant to vibration. Previously, coils with high resistance to vibration acceleration of 30 G or higher had an issue of not being able to support large current due to their low profile and small size. The developed power choke coil achieves a vibration acceleration resistance of 50 G or higher while also having excellent heat resistance and supporting large current, through the adoption of the company’s unique metal composite material, thereby contributing to the placement of automotive ECUs in the engine itself.
[Vibration durability conditions]
| Vibration acceleration | 50G (490 m/s²) |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 5 – 2000 Hz |
| Amplitude | 5 mm max. |
| Vibration directions, number of times (Time) | X, Y, Z directions, 108 times (equivalent to 100 h) |
| Temperature | 150°C (including product’s self-heating when energized) |
[Lineup] Mass production started in April 2018
Products with other inductance values will be launched during FY2018.
| Series | Case size (L×W)mm |
Inductance[6](*1) | DC resistance[7] 20°C | Rated current(*2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCC-M08**MS | 8.5 x 8.0 | 2.5~100uH | 7.4~302 mΩ | 12~5A |
| PCC-M10**MS | 10.9 x 10.0 | 0.33~100uH | 1.0~208 mΩ | 33~2A |
- (*1): Measured at 100 kHz
- (*2): Current value that causes a temperature rise of 40°C
[Term Descriptions]
- [1] Power choke coil
- This is an electronic component used in DC/DC converter circuits, etc., that serves as a filter for accumulating energy and removing noise.
- [2] integration of mechanical and electronic in-vehicle components
- This refers to the integration of mechanical drive components and the automotive ECU. Mechanical drive components and the automotive ECU used to be installed separately but were interconnected via cables. Demand for high-precision control, a higher degree of freedom in component layout, reduction in number of cables, etc., has led to the adoption of an integrated configuration of mechanical and electrical components.
- [3] DC/DC converter circuit
- This is a circuit that converts direct current from one voltage to another.
- [4] Self-resonant frequency
- An inductor has a natural frequency, and this frequency is referred to as self-resonant frequency. When the frequency of vibration conditions externally applied is in the vicinity of the self-resonant frequency, stress with several to several tens of times of applied acceleration is applied on the inductor, significantly deteriorating the vibration resistance.
- [5] Metal composite material
- This refers to a magnetic material made by compression molding of metallic magnetic material-based (iron group) powder insulated with resin.
- [6] Inductance
- This is an indicator of coil performance. Passing a changing current through a coil will generate a voltage that passes current in a direction that hinders the current change. The degree of the generated voltage is referred to as inductance.
- [7] DC resistance
- DC resistance is a resistance component of a winding (copper wire). The lower the DC resistance, the smaller the power loss. The lower the DC resistance, the smaller the loss, thereby improving power supply efficiency.