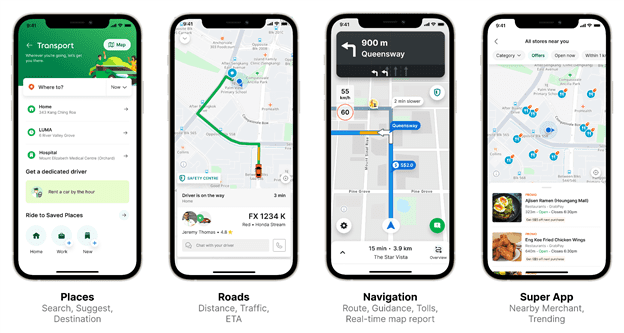
Grab launches GrabMaps as a new enterprise service, with GrabMaps already fully powering Grab services in 7 out of the 8 countries it operates in.
- Launches GrabMaps as a new enterprise service, giving businesses the opportunity to leverage the same location-based intelligence and technology powering its regional superapp
- GrabMaps already fully powers Grab services in 7 out of the 8 countries it operates in
SINGAPORE, June 8, 2022 – Grab Holdings Limited (NASDAQ: GRAB) today announced the launch of GrabMaps, a new enterprise service that will allow the company to tap into the US$1 billion market opportunity in Southeast Asia per year for mapping and location-based services. First developed for in-house use, GrabMaps was created to address Grab’s need for a more hyperlocal solution to power its services[1].
Today, GrabMaps provides location-based intelligence and services to all Grab verticals in 7 out of the 8 countries it operates in, and Grab expects to be fully self-sufficient[2] with GrabMaps by Q3 2022.
Tan Hooi Ling, Co-founder, Grab said, “Grab has always sought to build innovative tech that addresses Southeast Asia’s hyperlocal needs and GrabMaps is a great example of that. The back alleys and narrow side streets common across Southeast Asia cities often don’t show up on conventional maps, but are navigated by our driver and delivery partners every day. We’ve invested to turn this intelligence into a competitive advantage, allowing us to serve our users and partners with a great experience, at the same time driving efficiency and cost-savings for the business. We’re very proud that soon we will be fully self-powered by our own mapping and location-based technology. Commercializing this technology is another step forward for our young but fast-growing Enterprise and New Initiatives business.”
From driver/ delivery-partner allocations, ETA[3] calculations, route planning to delivery cost optimization and more, mapping technology and underlying points of interest (POI) and route intelligence are critical to the majority of core features that platforms like Grab rely on. GrabMaps today powers more than 800 billion API calls per month across a variety of Grab services. Based on a benchmark study of GrabMaps’ performance versus a leading third party mapping provider, GrabMaps had a 4x lower error rate and 10x lower latency[4]. Internal data also show that for countries that have moved completely to GrabMaps, the ease of finding the right POI for transport bookings improved by 3 percentage points on average, while ETT[5] accuracy improved by 1 percentage point regionally, with some countries seeing improvements of up to 7.8 percentage points.
GrabMaps powering the Grab superapp
Community-based Approach
GrabMaps’ core advantage is that it is built on the principles of community-based mapping that leverages Grab’s consumers, merchants, and fleet of driver and delivery partners. GrabMaps solutions draw from fresh data from millions of orders and rides served daily, with real-time feedback from partners on road closures, business address changes and more. Driver and delivery-partners also have the opportunity to contribute to our maps, collecting POIs and other rich data like street imagery, street names, traffic signs and more for additional income. This gives GrabMaps an edge in accuracy, coverage and freshness while being highly cost-effective.
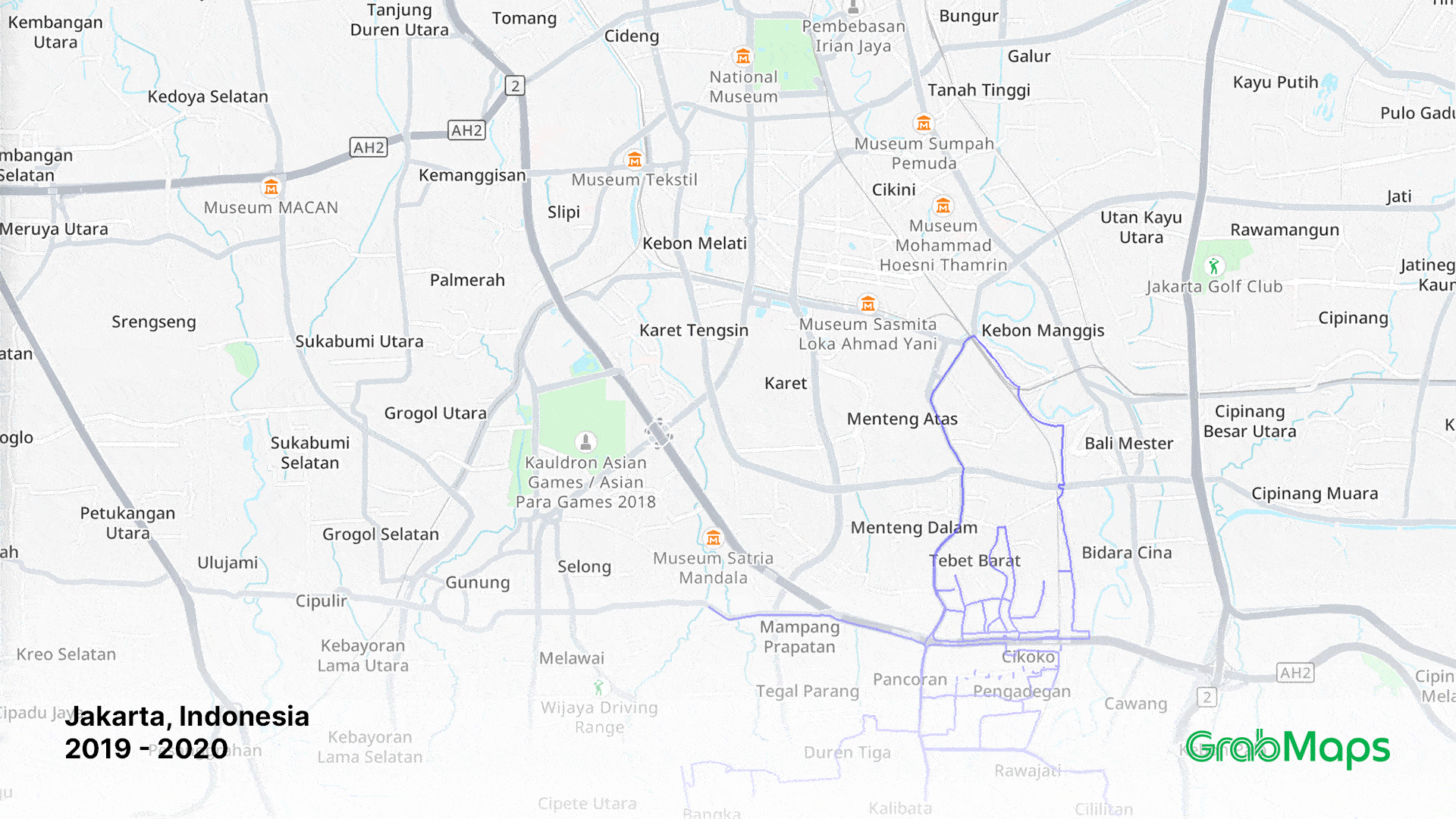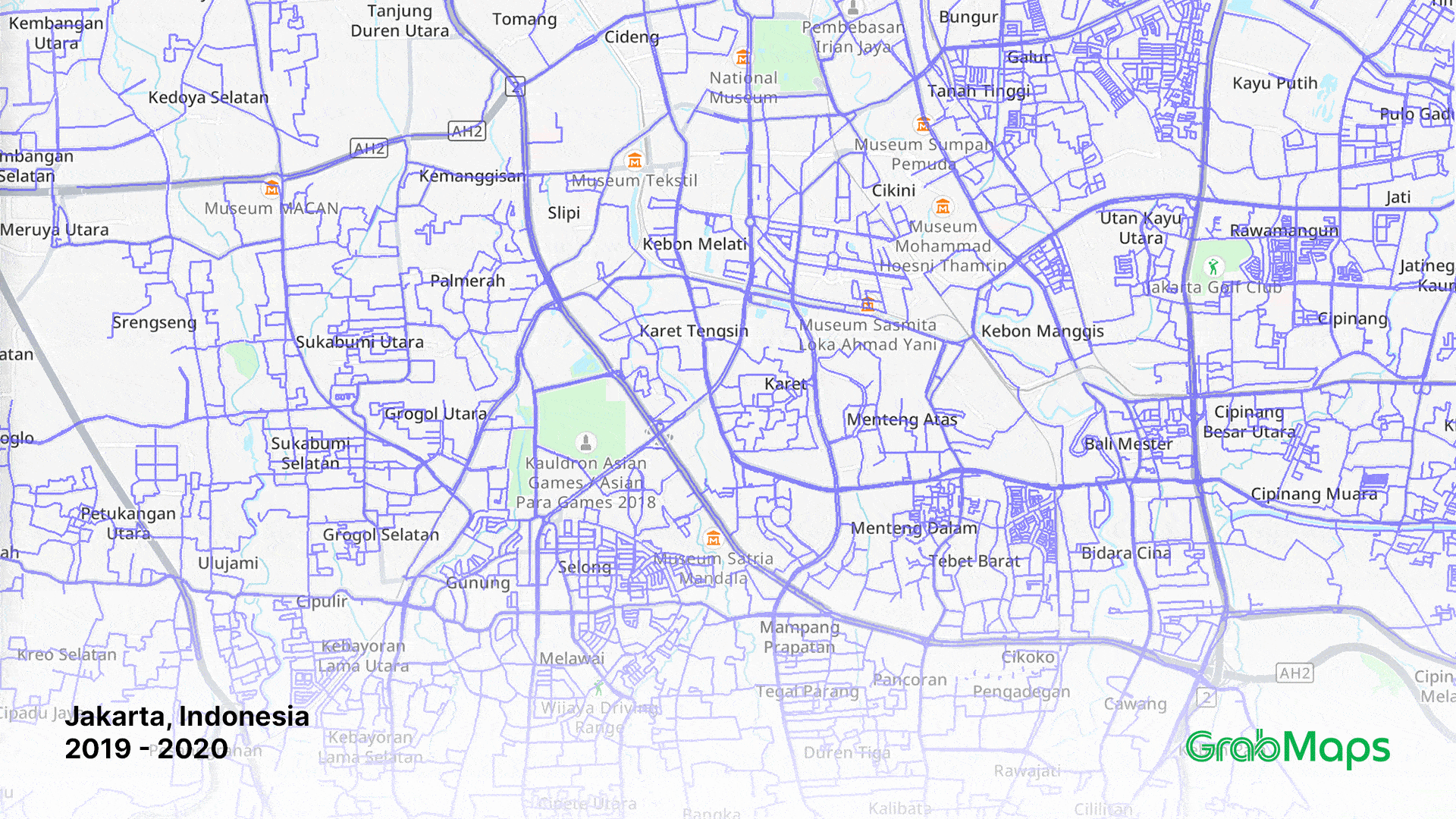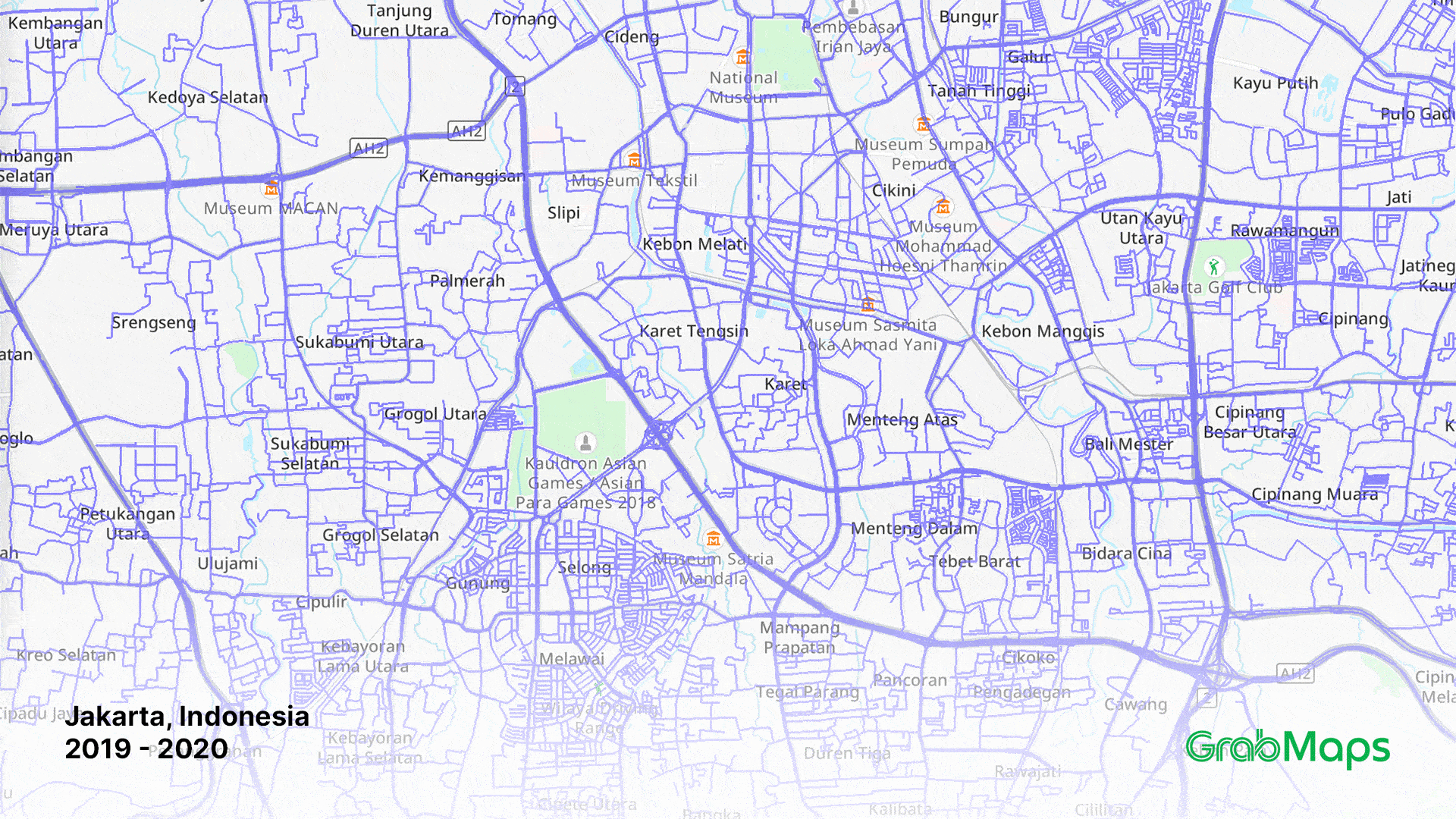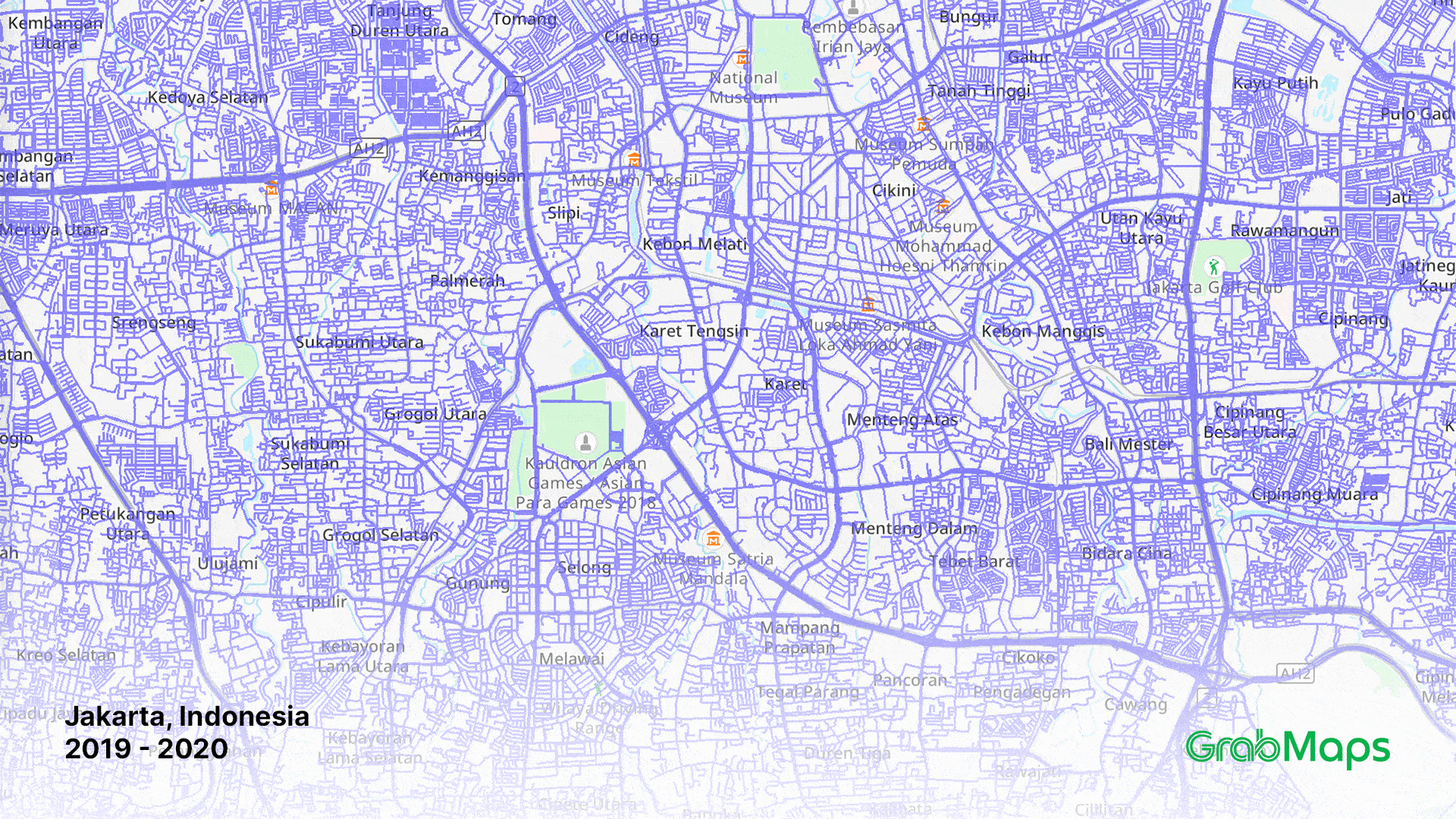
1-year growth in street imagery coverage in Jakarta on GrabMaps
Crowdsourcing map data through the KartaView app, as well as Grab driver and user superapp
GrabMaps for Enterprise
Many organizations utilize location-based services to varying degrees, including tech platforms, telcos, logistics companies and government agencies. GrabMaps as a B2B solution will offer the following services:
- Base Map Data allows companies to license data from Grab, such as Places, Road & Traffic, and Imagery, benefiting from a fresh and fast-growing set of map data in Southeast Asia with coverage from capital cities to tier 3 towns.
- Places: GrabMaps today has more than 33 million POIs and point addresses in Southeast Asia and expects to grow this to 37 million by the end of the year.
- Roads and traffic: Comprehensive view on road networks in Southeast Asia, and also rich data such as turn restrictions, speed limits, toll gantries and more.
- Imagery: High-resolution street level imagery that provides wide to 360 degree views from positions along roads. Available in a range of image resolution and quality.
- Map-making tools and software-as-a-service is an end-to-end stack that enterprise customers can leverage to build their own maps, anywhere in the world. Grab’s proprietary map-making camera, Kartacam, was designed to suit emerging market conditions. It is lower-cost while maintaining quality parity with conventional solutions. It is also easy to use, even for non-tech savvy operators such as Grab’s driver-partner fleet. Kartacam is currently being piloted by partner companies in Paris, Johannesburg, Dubai and Seattle.
- Application programming interface (APIs) and mobile software development kits (SDKs) that Grab plans to launch later in 2022 and in 2023 respectively, will allow developers and teams to enhance or build their own applications and geolocation capabilities leveraging GrabMaps technology, such as Grab’s routing, search, traffic and navigation features.

Kartacam in action
Philipp Kandal, Head of Geo, Grab said, “Grab is the region’s leading superapp, serving a wide range of daily needs for millions of consumers daily, and GrabMaps powers this. Our track record, as well as the unparalleled view we have on Southeast Asia, gives us confidence that GrabMaps can be the best map platform of choice for Southeast Asia.”
[1] The mapping market in Southeast Asia is estimated to approach US$1 billion per year by 2025. Source: Global Digital Maps Market 2019 – 2026, Verified Market Research
[2] Grab will no longer be dependent on paid map and location-based services from third party providers. Grab continues to use OpenStreetMap as its base layer map via an Open Database License.
[3] Estimated time of arrival
[4] Error rate is the % of times the API failed to return an accurate response. Latency is how fast the API serves a response.
[5] Estimated travel time
– End –
For press enquiries, contact:
For business enquiries, contact: