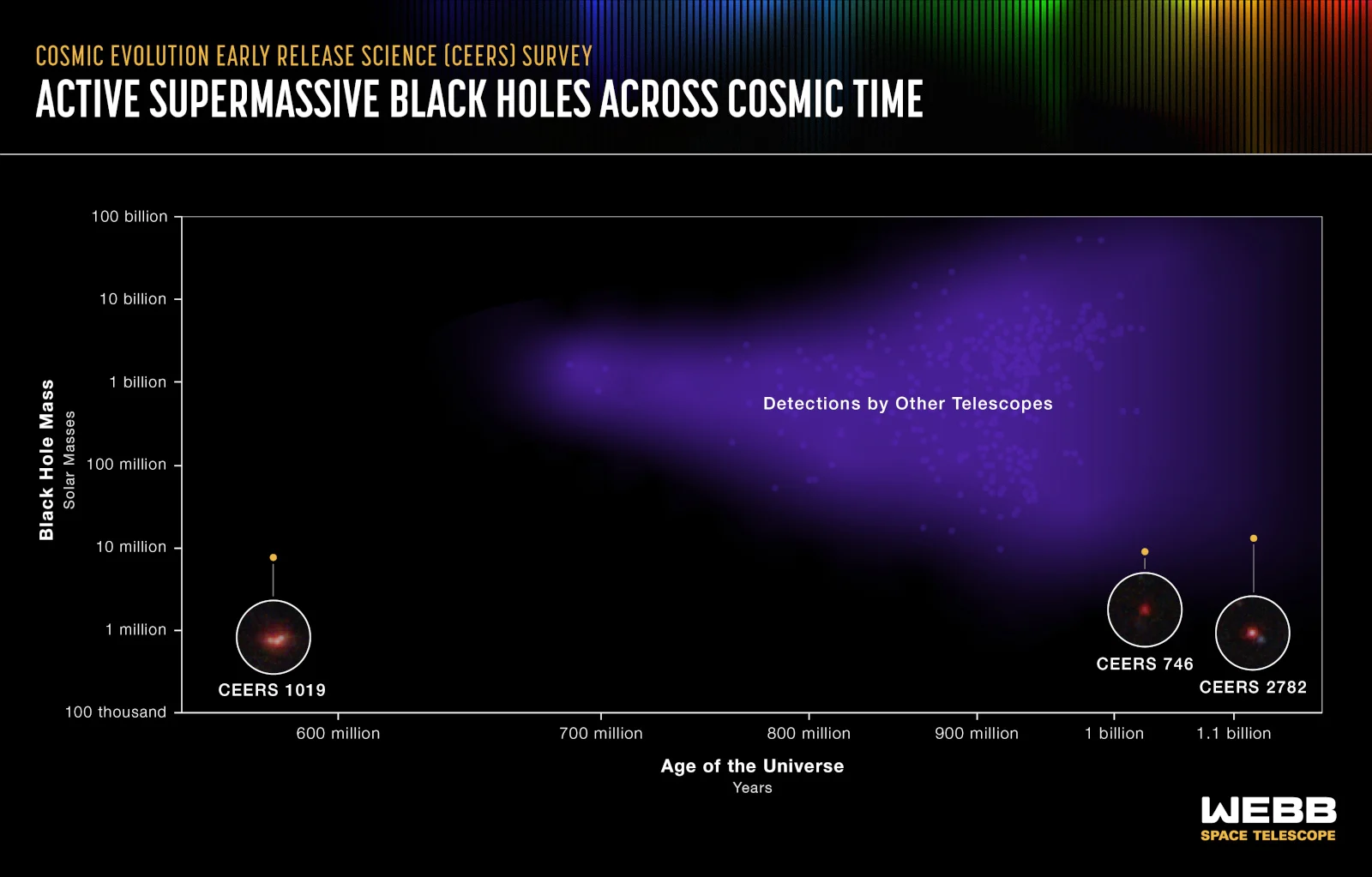
CEERS 1019 is much smaller than other ancient black holes previously discovered.
The James Webb space telescope has given scientists the capability to discover celestial objects they wouldn’t have been able to otherwise, such as ancient galaxies that theoretically shouldn’t exist. Now, as part of the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science (CEERS) Survey, researchers have discovered the most distant active supermassive black hole we’ve seen to date.
Thanks to the near- and mid-infrared images James Webb has taken, researchers were able to find a supermassive black hole in the galaxy they’ve dubbed CEERS 1019. They were also able to determine that the black hole has existed merely 570 million years after the Big Bang and that it’s around 9 million solar masses. In addition, the data provided by the telescope allowed them to come to the conclusion that the black hole is eating up a lot of gas and churning out new stars. “A galaxy merger could be partly responsible for fueling the activity in this galaxy’s black hole, and that could also lead to increased star formation,” CEERS team member Jeyhan Kartaltepe of the Rochester Institute of Technology in New York explained. In the image below, you can see CEERS 1019 appearing as three bright clumps.
NASA, ESA, CSA, Leah Hustak (STScI)
At 9 million solar masses, this black hole is much smaller than other active supermassive black holes previously discovered. Those celestial objects typically contain more than 1 billion times the mass of the sun, which makes them much brighter and easier to detect. The CEERS 1019 black hole is more similar to the one in the center of our galaxy, which is around 4.6 million times the mass of the sun. NASA said scientists have long known that smaller black holes must have existed earlier in the universe, but it wasn’t until James Webb became operational that they were able to confirm their presence.
In fact, the CEERS Survey team also found two other ancient but small black holes through their data. The CEERS 746 black hole existed 1 billion years after the Big Bang, while the CEERS 2782 black hole has been around since 1.1 billion years after the event. When viewed through other instruments, these black holes appear as ordinary star-forming galaxies. Astronomers are also reviewing other more distant black holes found using James Webb’s data at the moment, so CEERS 1019 might lose the record sooner rather than later.
CEERS team lead Steven Finkelstein from the University of Texas at Austin said: “Until now, research about objects in the early universe was largely theoretical. With Webb, not only can we see black holes and galaxies at extreme distances, we can now start to accurately measure them. That’s the tremendous power of this telescope.”
Scientists still find it difficult to explain how this black hole formed so soon after the universe began. But in the future, Webb’s data could give them the information they need to be able to figure out how early black holes are formed.