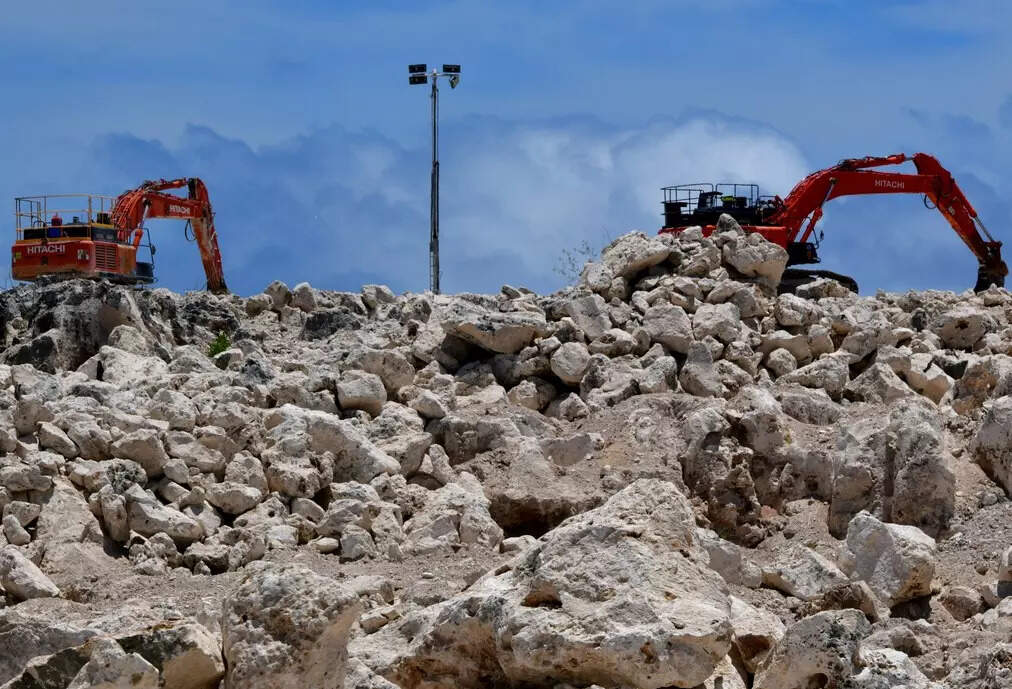
In a groundbreaking discovery, Norge Mining, a government organization in Norway, has unearthed extensive deposits of phosphate rocks within the country. This finding holds tremendous potential for the electric car industry, as these rocks can be utilized to power electric vehicles.
According to Norge Mining, Norway may possess up to an astonishing 70 billion tonnes of phosphorus, sufficient to meet the electric power demand for the next half-century.
Listed as a critical mineral by the European Union, phosphorus deposits in the Western Sahara region of Morocco. Reports say these are the largest known deposits of the mineral, totaling approximately 50 billion tonnes.
Substantial reserves have also been identified in China – approx. 3.2 billion tonnes – and in Egypt – 2.8 billion tonnes – according to the US Geological Survey (USGS).
Phosphorus is an exhaustible resource, predominantly consumed by the agriculture sector for fertilizer production, leaving a meager portion available for other industries. This overreliance on phosphorus for farming raises concerns about its availability for alternative sectors, potentially hampering the growth of specific crops.
Moreover, the use of phosphate fertilizers in agriculture has detrimental effects. Runoff from these fertilizers can result in algae blooms in rivers, posing a grave threat to freshwater ecosystems.
Notably, phosphorus plays a vital role in the production of lithium-iron phosphate batteries utilized in electric cars. With the global economy heavily dependent on roughly 50 million tonnes of phosphorus annually, the extraction and refinement processes have raised concerns due to their potential for significant pollution.
To address these concerns, Norge Mining has pledged its commitment to employing carbon capture technology to mitigate the carbon emissions associated with phosphorus extraction. Furthermore, the phosphate deposits discovered in Norway also contain valuable materials like vanadium and titanium, both classified as critical raw materials by the EU due to their limited availability.
In conclusion, the revelation of substantial phosphate deposits in Norway brings optimism for sustainable power generation in the realm of electric cars. Measures are being taken to minimize the environmental impact of phosphorus extraction, while the presence of other valuable materials enhances the significance of this resource. The newfound potential of Norway’s phosphate deposits stands as a promising step toward a greener future in the electric vehicle industry.