

As the world shifts towards electric vehicles (EVs), investments in EV charger infrastructure must follow suit. Current research predicts that 54% of new car sales and 33% of the global fleet will be electric by 2040. With this rapid adoption of EVs on a global scale, there is an increasing demand for EV charging stations.
A connected network of EV charging stations must be established for a complete and optimized EV charging experience. But what technologies should be used to connect this smart charging network? There are two popular options – Cellular Connectivity and Wi-Fi Connectivity.
Cellular Connectivity vs. Wi-Fi Connectivity
There are many technologies to choose from to give charge points Internet access. Most residential chargers use Wi-Fi, but Wi-Fi for EV chargers that will be used by the public require additional control and security. Chargers utilizing 4G LTE-based SIM cards have data security and privacy advantages over stations utilizing Wi-Fi connectivity. The 4G cellular network uses regulated, licensed spectrum bands that are highly reliable and less vulnerable to interference issues or outages. Another thing to consider is that Wi-Fi technology is dependent on the quality of the connection provided by local, public, or private networks.
Benefits of Cellular Connectivity for Commercial EV Chargers
When it comes to EV chargers, a reliable and secure connectivity source is vital. In terms of range, 4G cellular connectivity offers more coverage, even in remote locations, which is important as the need for EV chargers increases, and charger hosts seek to scale their charger network. Wi-Fi connected chargers have a smaller range of coverage because there are some areas where the signal strength may be weak or non-existent. The quality of the connection depends on the existing local, public, or private Wi-Fi networks. This can leave charger owners without control over the quality of the network or the choice of supporting routers and internet providers.
Commercial EV chargers are not immune to security threats, but some chargers are better equipped to handle threats than others. An EV charger that connects to a Wi-Fi network exposes both the charger and the Wi-Fi network to two-way security risks. The charger can be used by an outside security threat to steal Wi-Fi credentials and access sensitive information. Even private Wi-Fi networks can be compromised due to relaxed security practices such as relying on default Wi-Fi passwords or failing to update the network’s firmware. With 4G cellular connectivity, there are fewer security vulnerabilities. Cellular connectivity also provides enhanced security by separating the charger’s connection from the local Wi-Fi Internet infrastructure, which eliminates most security attack points.

Another advantage of 4G cellular is the opportunity for remote access to the charger. In commercial applications especially, remote access to an EV charger is key for utilizing current data analytics to optimize charger performance and maintenance cycles. With remote access, charger diagnostics can be acquired virtually, without requiring a technician to travel to the installation site. Charger owners can also monitor and control key charger operations, scale their EV network, and increase overall user satisfaction.
With mobile networks already established and providing comprehensive coverage on a global scale, 4G cellular connectivity is ideal for commercial EV charger applications.
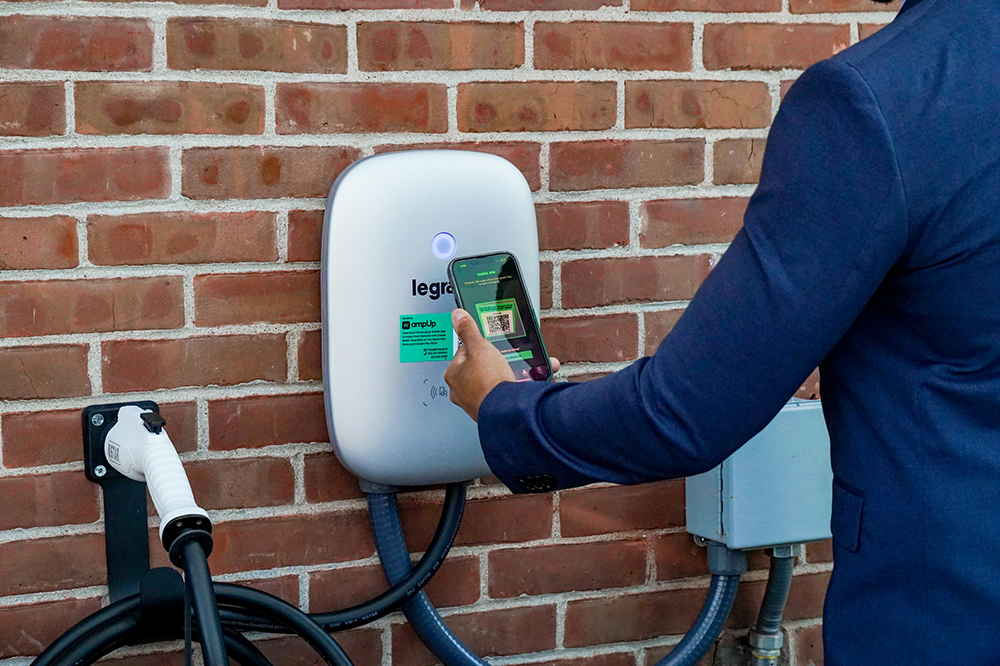
Ready to make a change? The Commercial Electric Vehicle Charger from Legrand is a Level 2 EV Charger that provides convenient access to electric vehicle charging. Legrand’s EV Charger is preconfigured with AmpUp Managed Charging Solution and offers exceptionally reliable data communication, robust security features, and remote access capabilities. To learn more about EV charging and Legrand’s commercial EV charging offering, visit Commercial Electric Vehicle Charging | Legrand.