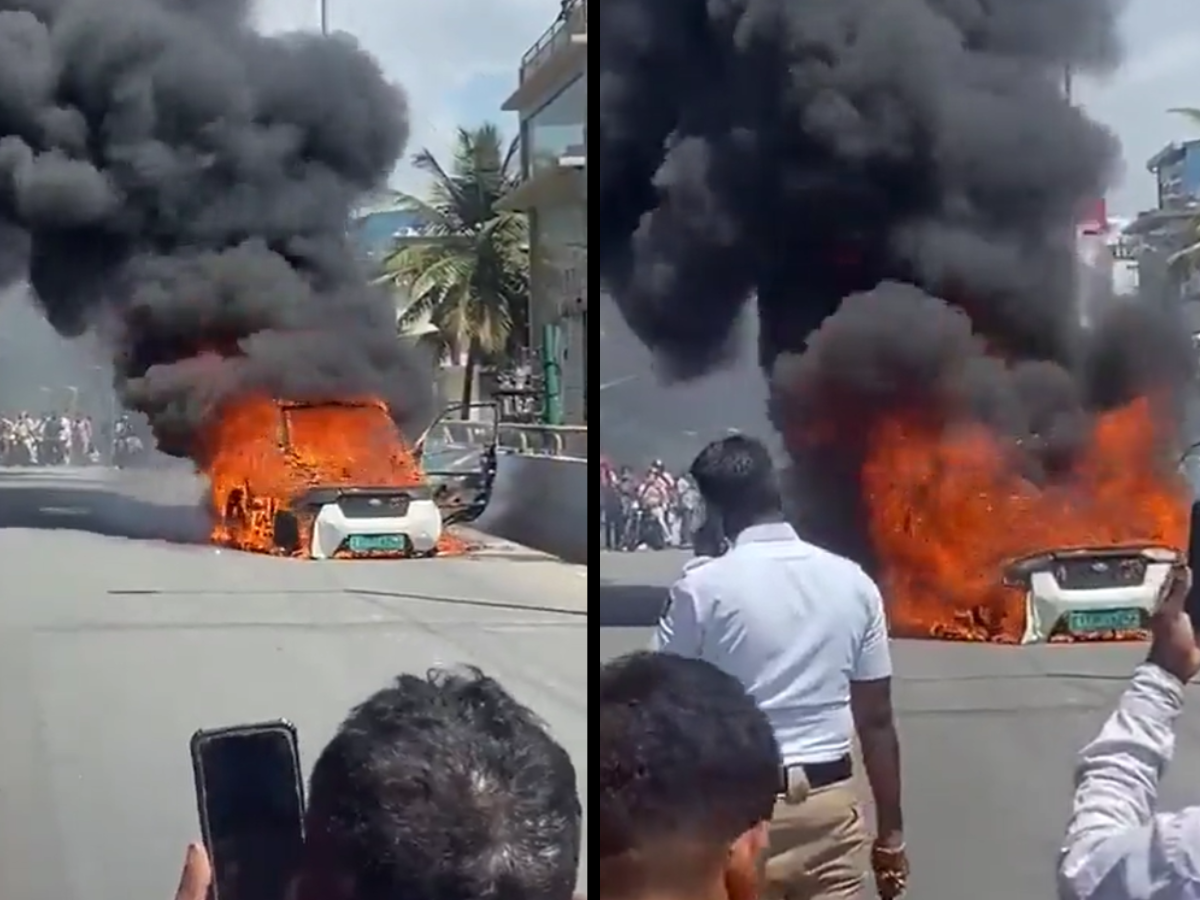
In a recent incident in Bengaluru, an electric car burst into flames near Dalmia Circle in the JPNagar area, creating a horrifying scene that has gone viral on social media. Fortunately, no casualties have been reported, but the cause of the fire remains unknown.
Electric vehicle fires, although rare in theory, often attract significant attention when they do occur. These incidents are primarily attributed to the high energy density of electric vehicle battery packs, which store a large amount of energy in a compact space. When the battery pack is damaged, an internal short circuit can trigger a chain reaction known as thermal runaway. During this process, the battery generates more heat than it can dissipate, leading to a fire.
About 95% of battery fires in electric vehicles are classified as ignition fires, producing jet-like directional flames. The remaining 5% involve a vapor cloud explosion. Several factors can cause a battery to catch fire, including physical damage from accidents, manufacturing defects, battery faults, workshop repairs, arson, external fires, or overheating.
Electric vehicle fires pose unique challenges. Once batteries catch fire, they can be difficult to manage. Lithium battery fires burn at extremely high temperatures, lasting for days and causing extensive damage. They often reignite even after appearing to subside. Improper management of these fires can result in the emission of highly toxic gases and chemicals for hours, emphasizing the need for properly trained firefighting crews.
To control such fires, methods include cooling the battery with water or using a crane to lift the vehicle and submerge it in a large water container. It’s crucial to handle these situations with care to ensure the safety of firefighters and the public.
Interestingly, e-scooters and e-bikes face a higher risk of battery fires compared to electric cars and trucks. This heightened risk is primarily due to poor-quality battery design and construction, as well as the use of unapproved chargers. Unlike e-scooters and e-bikes, electric cars and trucks feature more sophisticated designs with advanced cooling systems. These systems maintain the batteries at optimal temperatures during everyday driving and recharging, making them significantly safer than batteries in smaller electric vehicles.
As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, it becomes increasingly vital to address the potential risks associated with battery fires. Proper training, awareness, and adherence to safety protocols are essential to ensuring the safe use and management of electric vehicles, protecting both the environment and public safety.