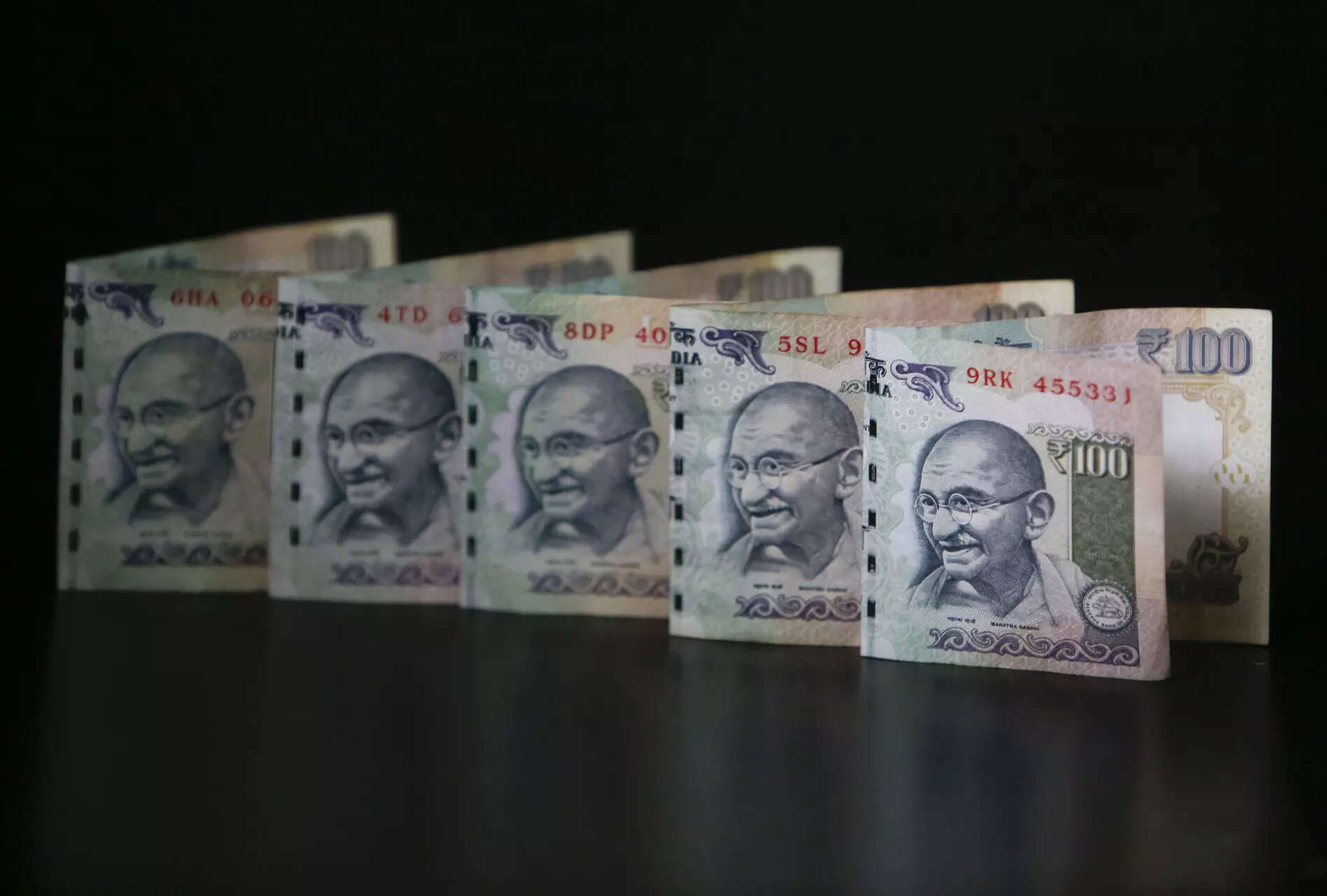
The Indian rupee was the most stable emerging market currency in the past year amid global economic uncertainty. What are the factors that contributed to its relative stability? It is largely the narrowing current account deficit (CAD), besides robust economic fundamentals. ET explains how the CAD influences the rupee movement and what are the consequences of a high deficit ratio.
What is the current account deficit?
A country’s current account is a calculation of the total value of goods and services imported and exported. If the value of goods and services imported exceeds the value of goods and services exported, then the current account turns into deficit mode. It considers the sum of trade balance and net income of companies from abroad. Current account deficit or surplus is expressed as a percentage of a country’s gross domestic product.
What is the relation between a country’s CAD and its currency?
When the current account turns deficit, then the country needs to pay more than it earns from the external sector. Therefore, there would be excess demand for foreign currency. In India’s case, a deficit means higher demand for dollars.
What is India’s current account deficit?
India’s current account deficit narrowed sharply to 1% of GDP in Q2FY24 from 3.8% in Q2FY23. This means the demand for dollar vis-a-vis rupee decreased when compared to a year earlier.
How did the rupee fare in 2023?
The rupee was one of the best performing currencies and the least volatile among global peers in 2023. The rupee opened at 82.66 against the dollar on January 2, the first trading day of 2023, and closed 0.6% weaker at 83.15 on December 29, the last trading day of the year. This was despite strengthening of the US dollar amid lingering geo-political concerns.
What are the prime reasons behind the rupee’s strength?
According to the Reserve Bank of India, much of the stability of the rupee is owed to the country’s sound economic fundamentals, including easing current account deficit. “Its relative stability in the recent period, despite a stronger US dollar and elevated US treasury yields, reflects the strength and stability of the Indian economy, its sound macroeconomic fundamentals, financial stability and improvements in India’s external position, particularly the significant moderation in the current account deficit, comfortable foreign exchange reserves and return of capital inflows,” RBI said.
Is India’s current account deficit manageable?
According to the World Bank, India may receive an estimated $135 billion in inward remittances in 2024 and it would remain the largest recipient of remittances globally. This, along with strong foreign direct investment inflows would make the financing of the current account deficit easier. “Thus, the CAD for 2023-24 and 2024-25 is expected to be eminently manageable,” RBI said, helping the currency market sentiment improve. India’s foreign exchange reserves at a healthy $622.5 billion, which can cover over 10 months of imports, also lends support to a stable currency outlook.