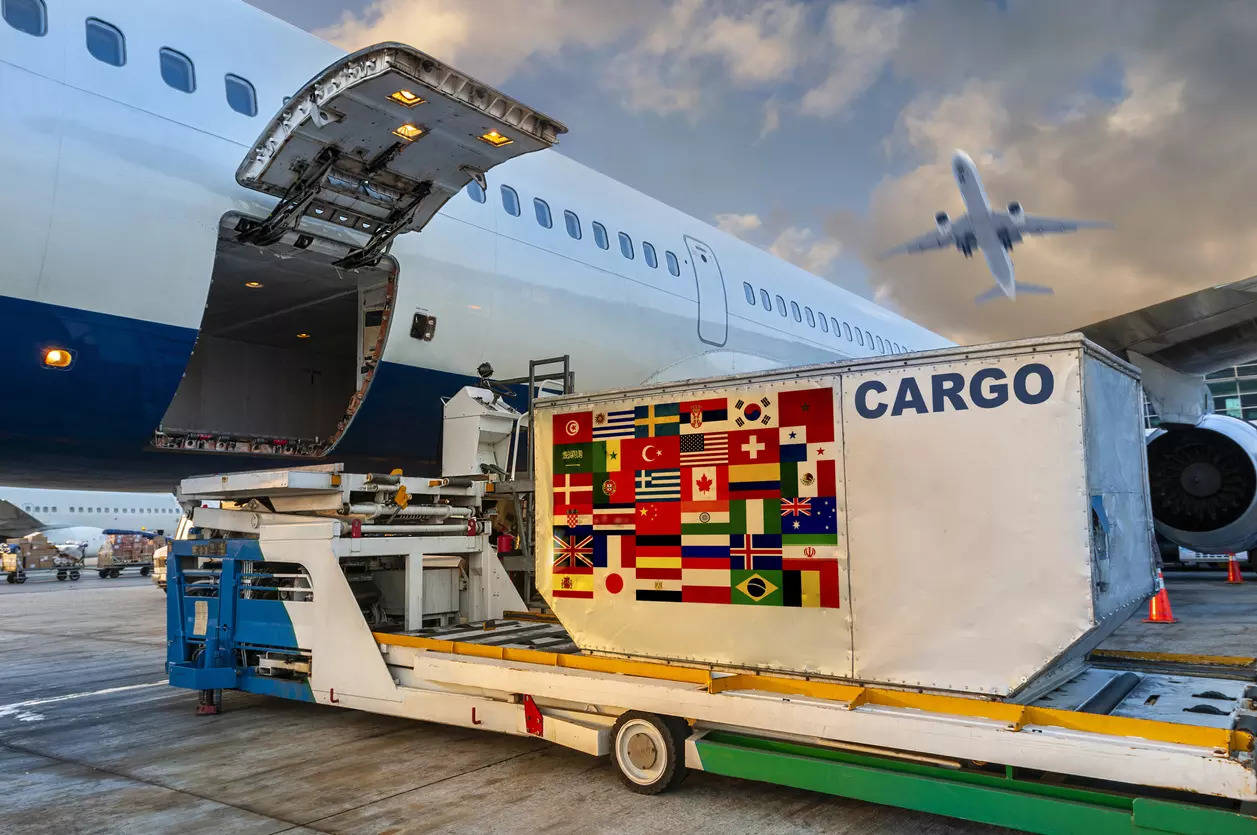
India will allow foreign airlines to operate non-scheduled cargo flights from all airports in the country for three years, lifting 2020 curbs that had restricted them to six–Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Kolkata and Chennai. This followed lobbying by exporters against the restrictions.
While India had an open sky policy in air cargo that allowed unhindered movement by foreign airlines, the government amended it in 2020 to give Indian carriers a boost. With minimum earnings from passenger flights due to the pandemic at the time, they depended on cargo to make money.
However, exporters have been protesting that goods capacity had shrunk as Indian carriers failed to deploy enough aircraft to meet demand.
“The open sky policy for foreign cargo carriers has been reviewed by the government,” the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) said in a circular issued on 2 February . “The operations of foreign and non-scheduled freighter charter service shall be allowed at all international airports for a period of three years to facilitate air cargo movements and to give sufficient time to Indian carriers to develop their capacity.”
Exporters had repeatedly asked for the policy to be reversed as the cost of ferrying perishables such as marine products shot up. They told the commerce ministry that the move was having a detrimental impact on India’s exports, hitting foreign exchange earnings, said people familiar with the matter.
“We mostly deal in perishables like marine products, which have a huge market in Europe and use the capacity of foreign airlines–Emirates, Qatar Airways–to increase our reach,” said an exporter from Kerala. “Indian airlines neither had the capacity nor the network to ferry such products. So the products had to be carried to Chennai by truck, which itself took more than 12 hours. This was not feasible for time-bound products like ours.”
SpiceJet and IndiGo were among local carriers that converted passenger aircraft into cargo planes and sought to induct freighters in order to take advantage of the boom in air cargo. At the time, Covid-19 had grounded passenger planes, which carry cargo in the belly, hitting supply chains.
While SpiceJet formed a separate company for air cargo, IndiGo decided to induct four freighter aircraft. IndiGo has over 60% share of India’s passenger market.
However, with planes returning to the air, cargo rates dropped significantly as there was excess capacity. IndiGo has slowed its freighter plans, having inducted three of them till date. SpiceJet has also cut down its cargo operations.
“This decision of DGCA is a pivotal step that will elevate air cargo activity in India,” said Mahesh Fogla, executive director, Patel Integrated Logistics Ltd. “This move will open doors for all cargo operations to all international airports. Additionally, it will lead to economic growth and growth in trade activities across non-metro cities as well as giving a boost to air-freight capabilities.”
Following the change in policy, foreign airlines are now looking to restart cargo operations in India. Emirates SkyCargo is planning to add three new cities to its network by June. India is among the top five cargo markets for Emirates.