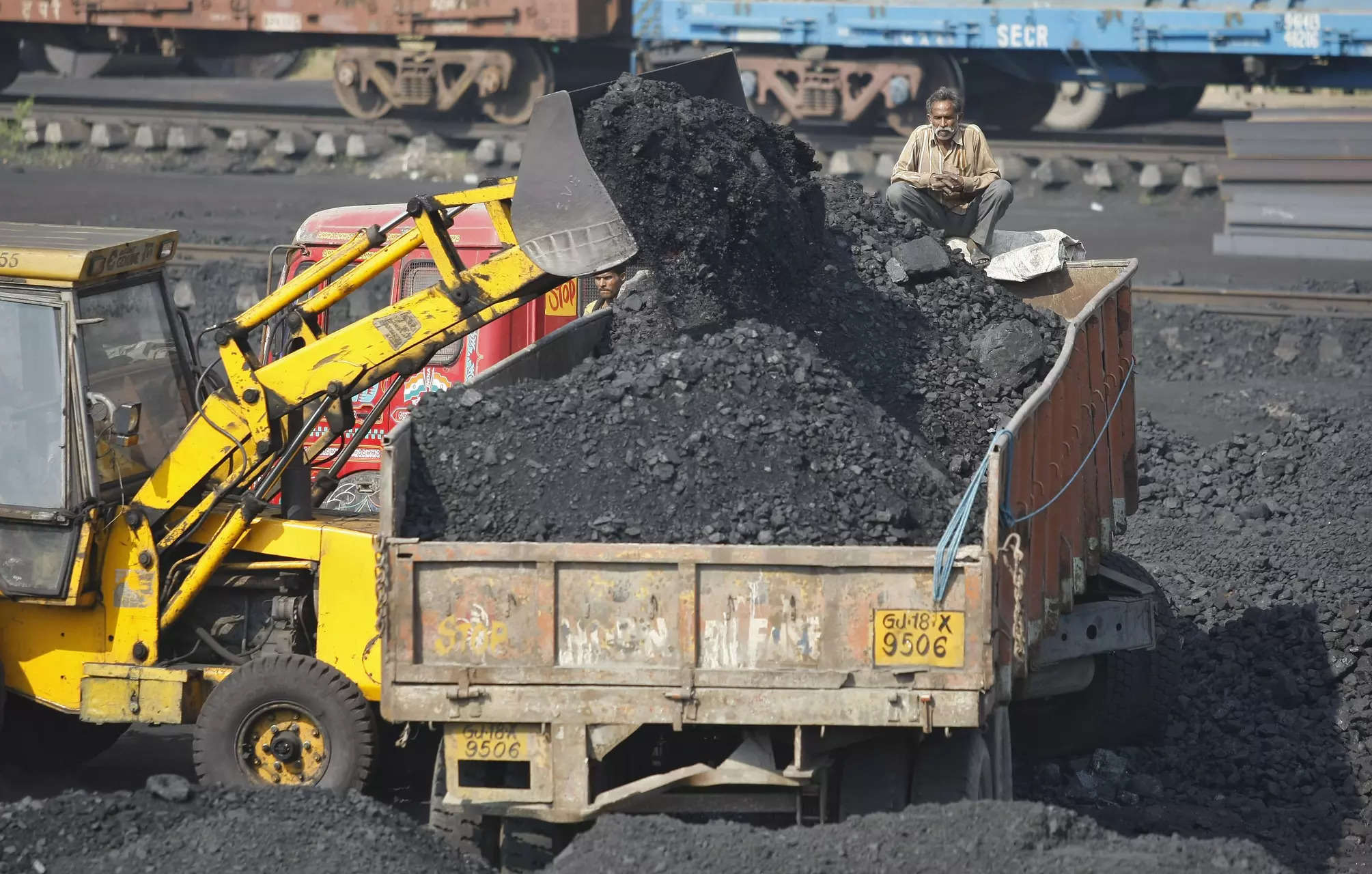
More than two years after climate negotiators first attempted to consign coal to history, the dirtiest fossil fuel is having a moment.
Thanks to a combination of China’s energy insecurity — pushing Beijing back to trusted power sources — plus rising Indian demand, the continued fallout from the war in Ukraine and faltering international programs to wean developing economies off fossil fuels, coal is proving remarkably resilient. Output hit a record last year, and producers are preparing for a future where they will be required for decades yet to balance renewable energy.
Even prices are holding up. While thermal coal is trading at just a fraction of the lofty levels reached in 2022, after Russia’s invasion of its neighbor, prices are still well above historic norms. Benchmark Newcastle coal futures are changing hands just under USD 130 a ton, roughly a quarter of the peak but higher than any level between 2011 and 2020.
Much of this second wind is down to Asia. In 2000, the International Energy Agency estimated advanced economies accounted for almost half of coal consumption. By 2026, China and India alone will make up more than 70%. Those two heavyweights and Indonesia started operating new coal power plants amounting to 59 gigawatts last year, and either launched or revived proposals for another 131 gigawatts — about 93% of the world’s total, according to Global Energy Monitor.
“You look at Asia, the demand and the build out of coal-fired power plants, particularly in India — coal’s not going anywhere anytime soon,” Rob Bishop, chief executive officer of Australian miner New Hope Corp., said in an interview.
The extended final act will be a vindication for fossil fuel executives, who have long argued against the feasibility of shifting swiftly out of carbon-intensive power, pointing out benefits in terms of reliability and cost. A mention of coal’s buoyancy earned Saudi Aramco CEO Amin Nasser a round of applause at a major energy conference in Houston last week.
It’s less good news for efforts to curb carbon emissions and reach global climate goals.
For years, analysts expected coal production to plateau after it hit a then-record in 2013. Funding, after all, was drying up. Then came 2021, when power shortages in China set Beijing on a path to order more mining to ensure energy security.
In 2022, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and blackouts during heatwaves in India further bolstered coal demand. By last year, output had risen to a record 8.7 billion tons, according to the IEA.
That figure is expected to drop this year. But the agency expects it to stabilize through 2026 — in line with industry forecasts of a long goodbye.
All of this is visible on the ground. In China, which produces and consumes half the world’s coal, miners are struggling to maintain growth rates after boosting output 21% over the past three years to 4.7 billion tons. Low-cost reserves have mostly been tapped, leading companies to dig deeper, more expensive mines. Fatalities have also started rising after years of declines.
Record amounts of new solar panels and wind turbines, along with a rebound in hydropower and steadily growing nuclear generation, mean low-carbon energy will likely exceed the growth in electricity consumption, according to the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air.
But that clean energy will also be coal’s lifeline, said Zhang Hong, deputy secretary-general of the China National Coal Association. Renewable power only generates when weather permits, so even as other baseload options emerge, cheap and reliable coal will still play a role.
“The next 10 to 15 years will remain a crucial strategic window,” Zhang said.
India is the one country where the IEA forecasts coal output to grow this year, with production set to top 1 billion tons for the first time. Prime Minister Narendra Modi needs to meet growing energy demand while reducing reliance on expensive imports. Yet even after a surge in renewables, nuclear, hydropower and other baseload options have fallen short — so coal is expected to remain the dominant source of power at least until the end of this decade.
Indonesia, meanwhile, the world’s top thermal coal exporter, sees production stable for the next two years. That’s partly to feed surging domestic demand from a booming, power-hungry nickel processing sector, even if lower prices eventually cool enthusiasm.
But it’s also evidence of the difficulty of accelerating the end of coal where economies have newer plants, rising energy demand and an urgent need to create jobs. In 2022, Jakarta agreed to a USD 20 billion green deal with wealthy governments and financial institutions that would, among other things, close coal power stations early. Coal phaseouts, however, have proved far more challenging than anticipated. Landmark deals remain on the negotiating table.
Coal’s days are numbered, of course. Advances in solar and wind have made those technologies far cheaper than coal power in most parts of the world, and similar gains for batteries and energy storage systems could finally make around-the-clock renewable power affordable enough to transform the energy mix.
But for now, the transition is testing years-long expectations of rapid peaks and subsequent steep declines.
“We see that the world needs more operators to mine coal and support the transition over many decades to come,” New Hope’s Bishop said.