Read by: 100 Industry Professionals

New Delhi: The global automotive industry is rapidly adopting cutting-edge technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning as part of the Industry 4.0 evolution. This shift is driven by the need to enhance production efficiencies and eliminate human error in complex manufacturing processes. According to GlobalData, significant advancements like AI integration, 3D printing, and vehicle electrification are transforming automotive manufacturing and the supply chain.
GlobalData’s Automotive Project Manager, Vivek Kumar, highlights the multifaceted role of AI in automotive manufacturing. “AI is integrated into various stages of product development, from design to the assembly of the vehicle. The incorporation of AI enhances the creation of alternative and more efficient vehicle designs, streamlines prototype development, optimizes production and assembly processes, and improves vehicle testing. Additionally, AI plays a crucial role in supply chain management, ensuring a seamless and efficient workflow throughout the entire development cycle.”
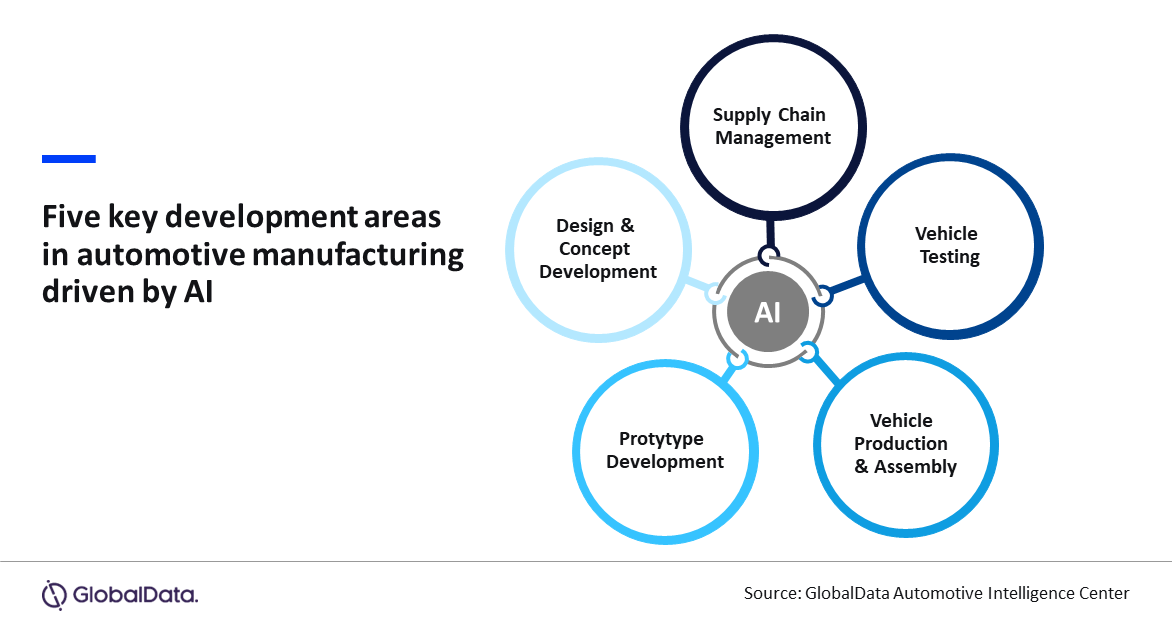
Kumar further elaborates on how AI-generated design algorithms benefit vehicle manufacturing. “The integration of AI in automotive manufacturing has significantly boosted production efficiency. Manufacturers use AI-generated design algorithms to explore multiple design possibilities, optimizing vehicle weight, strength, packaging, and performance. This leads to the creation of lighter, more efficient vehicles.”
In addition to AI, the use of robotics and automation is transforming the manufacturing landscape. AI-powered robotic machines can perform complex, labor-intensive tasks more effectively than human workers. This not only improves the quality of manufacturing but also reduces wastage and increases output, making the processes more efficient and cost-effective.
3D printing is another revolutionary technology reshaping the automotive industry. It accelerates the prototyping and production phases, reduces material waste, and lowers overall production costs. This technology aligns with the industry’s goals of sustainability and performance enhancement.
“In the near term, 3D printing will significantly impact manufacturing methods by supporting rapid prototyping and challenging traditional approaches that rely on specialized tools and lengthy production times. It also enables the development of complex components and customized parts that are often difficult to produce using traditional methods,” Kumar said.
The transition towards electric vehicles (EVs) is also a critical aspect of this technological evolution. EVs have fewer components than internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, which will impact the variety and quantity of parts produced by suppliers. This shift necessitates adaptation, particularly in terms of workforce skills in high-voltage systems and electronics.
“These manufacturing trends are driving changes in every aspect of the automotive industry, fundamentally transforming its foundation. The future of the automotive industry lies in the seamless integration of advanced software solutions, driving sustainable growth and innovation across all facets of the business. Over the next five years, significant improvements in the automotive manufacturing and supply chain will be required to accommodate this development at the vehicular level,” Kumar concluded.