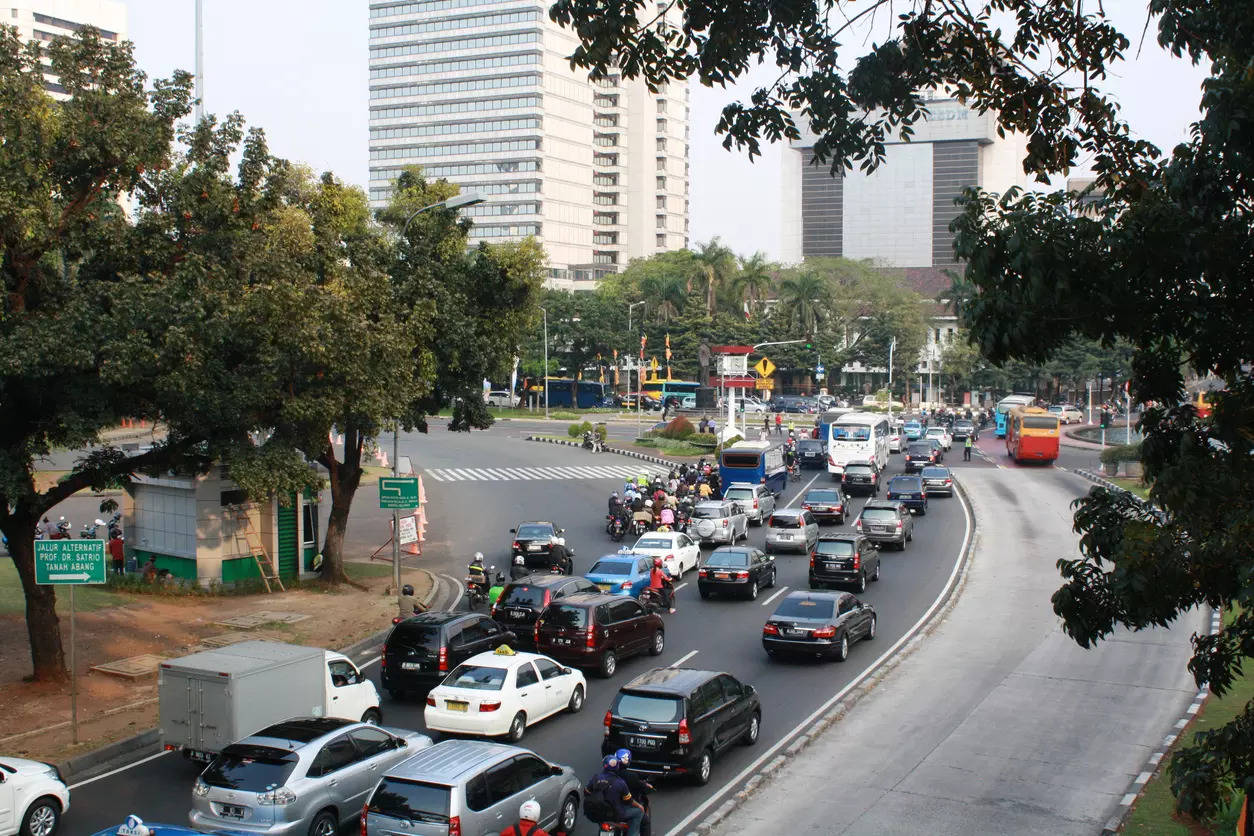
New Delhi: Around 44% of roads in Delhi have no footpath and only a little over one-fourth of the existing ones meet the width and height norms prescribed by the Indian Road Congress (IRC), according to a report released by IIT-Delhi.
These details, highlighted in the India Status Report on Road Safety released on the eve of the World Safety Summit in Delhi on Monday, come at a time when there is much talk and discussion about making the national capital safer and more pedestrian-friendly.
Quoting the findings of the audit carried out in Delhi this year, following an order by the Supreme Court Committee on Road Safety, the report mentions that compliance with the mandatory helmet-wearing rule is better on urban roads in the national capital, where more than 88% of two-wheeler drivers and pillion riders wear helmets. However, on rural roads, around 65% of two-wheeler drivers and 31% of pillion riders wear helmets.
The report also mentions the findings of the study of FIRs lodged by Delhi Police in 2019, 2021 and 2022, highlighting how nearly 44% of the people killed in road crashes in the capital during these three years were pedestrians, followed by two-wheeler riders (40%). According to the analysis, a significant 45% of vehicles involved in road fatalities were recorded as ‘unknown’ in FIRs, while another 18% were trucks, and 14% were cars.
“These details simply show that we must set quantitative targets for reducing risk to pedestrians and motorised two-wheelers users as the immediate priority in Delhi and other states and UTs as well,” said Geetam Tiwari, professor at Transport Research and Injury Prevention Centre at IIT, Delhi. Pedestrians, cyclists and two-wheeler riders are catergorised as the most vulnerable road users (VRUs).
The FIRs filed in 2020 were not included in the analysis since it was a pandemic year — the number of road crashes was lowest due to traffic restrictions during that year.
Road safety activists Prerna Arora Singh and Sarika Panda Bhatt asked if govts can build wider highways and city roads why can’t they provide safe and comfortable space for pedestrians. “Cities can be pedestrian-friendly when we provide safe and required space for people to walk,” said Bhatt who spearheads the Raahgiri in the National Capital Region (NCR).
Besides Delhi, the FIRs filed in five other states — Chhattisgarh, Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Maharashtra and Uttarakhand — were also studied to find the share of victims under different categories of road users and the impacting vehicles as well.
“Though reliable crash data are a prerequisite for effective safety programs, India does not have a reliable crash surveillance system. Therefore, this report presents an analysis of data extracted from FIRs… Additionally, this report summarises results from audits of the compliance of states with Supreme Court directives to establish robust road safety governance frameworks, including institutional arrangements, infrastructure enhancements, enforcement measures, educational initiatives, and medical care improvements,” the report said.
It said motorcyclists face very high risks across the country. In contrast, occupants of four-wheeled vehicles were much less likely to die, but these vehicles were involved as impacting vehicles at high rates. Nearly 44% of Delhi roads have no footpath and only a little over 25% of the existing ones meet the width and height norms prescribed by Indian Road Congress, says an IIT-D report.