With the advent of self-driving vehicles, GPS accuracy is becoming increasingly important and Tesla believes that it developed a technology that allows for a more accurate positioning by sharing data between vehicles, according to a new patent application.
Tesla’s latest patent application called ‘Technologies for vehicle positioning’ was filed last year and made public this week.
In the application, Tesla describes a problem with the accuracy of GPS positioning:
“For example, a smartphone with a positioning receiver may be able to determine its position to within five meters of the smartphone. The accuracy of the position determination may worsen when the receiver is in proximity of buildings, bridges, trees, or other structures. Although this may be sufficient for some positioning applications, greater accuracy is desirable for other applications, including autonomous driving. Accordingly, there is a desire to provide greater positioning accuracy despite the factors that affect the signals from the navigation satellites.”
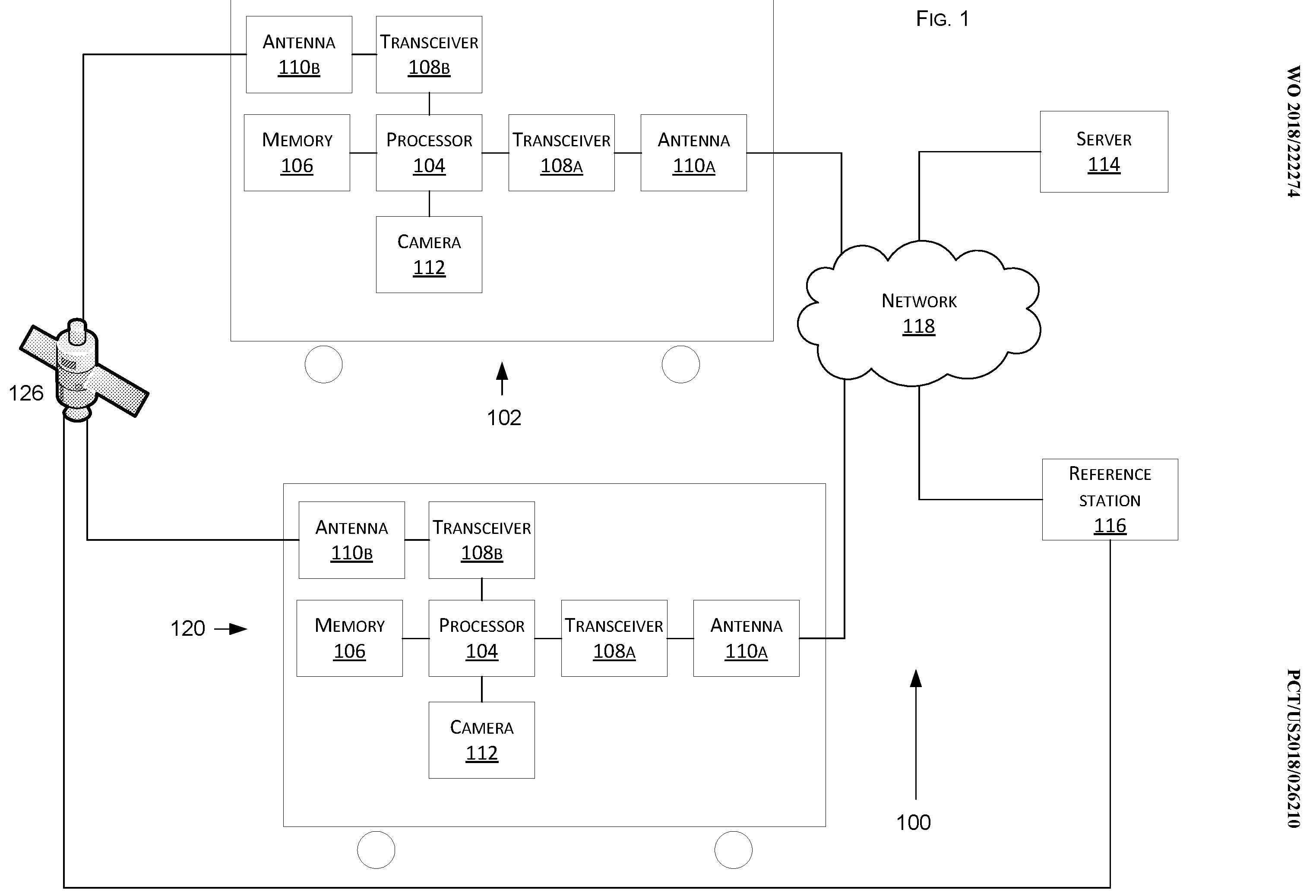
Tesla’s patent offers several solutions involving cameras detecting matching locations and using other vehicles in its fleet as “cooperative reference station” to share raw GNSS data and make positioning corrections.
They describe the technology in the patent application:
“It improves positioning accuracy despite the factors that affect the signals from the navigation satellites. The inventions increase such positioning accuracy via determining and applying offsets (corrections) in various ways, or via sharing of raw positioning data between a plurality of devices, where at least one knows its location sufficiently accurately, for use in differential algorithms. For example, some of such techniques can include (a) a reference station sharing a positional offset with an automobile, (b) a reference station calculating and sharing a set of parameters (offsets/corrections) for various error components including atmospheric, orbital, and clock, and/or (c) a reference station sharing its raw GNSS data so that vehicles can remove errors through differencing, or other calculations.”
Without necessarily sharing data between vehicles, Tesla also found a way to correct GPS data using other sensors.
The company describes matching camera data with vision maps in order to detect the exact location of a vehicle:
“The camera can detect a geometry of a boundary of a lane, as known to skilled artisans, on which the vehicle (102) or the vehicle (120) is travelling. This functionality has a beneficial utility because such detection can be used in a vision-map matching localization approach, as disclosed herein, where a location estimate is varied until the location estimate makes a camera-reported lane boundary coincide with a map-reported lane boundaries.”
The solutions would enable Tesla vehicles to have more accurate positioning data even where the GPS signal is not as strong as they would like.

This more accurate positioning system would be especially useful for autonomous driving applications and Tesla clearly intended it to be used by its Autopilot system since all the inventors listed on the patent applications were part of the Autopilot team at the time.
Here’s the full patent application: