Nissan Motor Co and Kobe Steel have today announced that Nissan plans to use ‘Kobenable Steel’ for Nissan models from January 2023 onward. With this Nissan becomes the latest global carmaker to confirm future use of low-carbon steel. Ford, Mercedes-Benz and BMW are among the other carmakers who have already inked similar measures.
Kobenable steel, commercialised by Kobe Steel, is claimed to significantly reduce CO2 emissions in the blast furnace process. Kobe Steel will also supply Nissan with aluminium sheets made from green-aluminium raw materials. This will be the first time Kobenable Steel will be used in mass-produced vehicles.
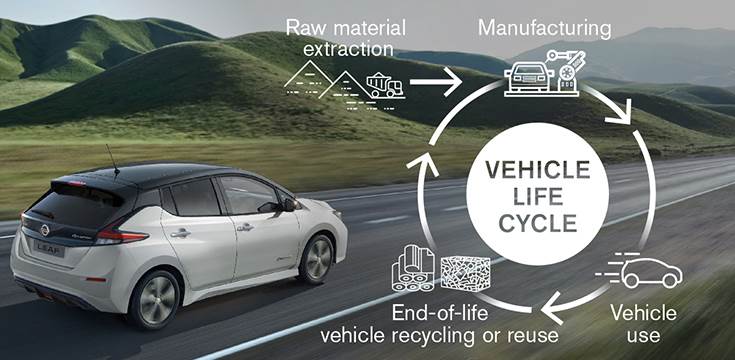
Nissan aims to achieve carbon neutrality throughout the entire product lifecycle, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, use, and the recycling or reuse of end-of-life vehicles, by 2050.
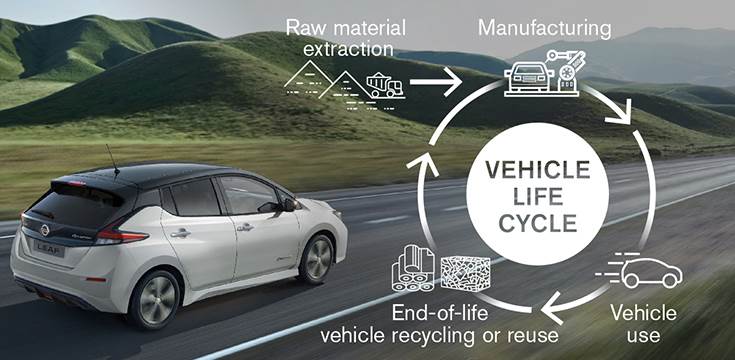
Nissan is targeting carbon neutrality across the company’s operations and product lifecycle by 2050. As part of this effort, by the early 2030s every all-new Nissan vehicle offering in key markets will be electrified.
As per the Japanese carmaker, since approximately 60% of a vehicle’s weight is made up of steel parts and around 10% of its weight is made up of aluminium parts, the use of green steel and green aluminum is a very effective way to reduce CO2 emissions during parts manufacturing, which is part of the vehicle’s lifecycle.
Therefore, the companies’ decision to use the steel and aluminium for Nissan vehicles is due not only to the significant CO2 emission reductions but also because the same level of high quality as conventional products can be achieved.
Nissan models will use Kobenable Premier, which reduces 100% of CO2 emissions during manufacturing through the mass-balance method. The specific amount of steel to be used by Nissan will be determined through further discussions.
The green aluminium raw materials purchased by Kobe Steel to produce aluminum sheets for Nissan are electrolytically smelted using only electricity generated by solar power, thereby reducing CO2 emissions during aluminium ingot production by approximately 50%. Recycled aluminum materials generated at Nissan’s manufacturing sites will also be used to further reduce CO2 emissions during production.