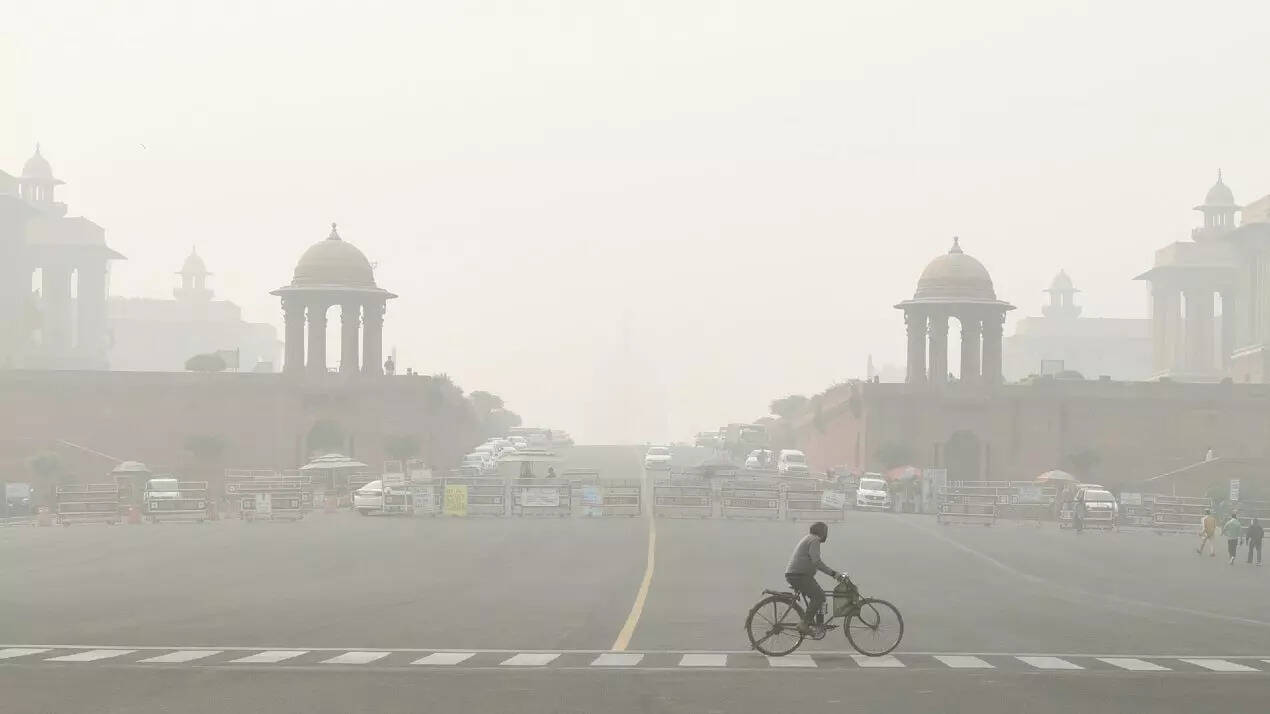
A new study by the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, has revealed a 15-26% drop in PM2.5, or extremely small, respirable pollutant particles, at three clusters in the city by tackling dispersed air pollution sources in the city. Dispersed sources of pollution, including unpaved roads, illegal dumping of construction waste, garbage burning, and broken footpaths, are major causes of air pollution.
The IIT-D study, titled ‘The Impact of the Dispersed Sources Programme on Local Air Quality‘, evaluated the impact of the dispersed sources on reducing PM2.5 locally. Under the guidance of Commission for Air Quality Management, A-PAG (Air Pollution Action Group), a foundation roped in by CAQM to work on dispersed sources of pollution, ran a programme in partnership with urban local bodies. It focused on identifying and resolving civic issues, both short-term such as illegally dumped garbage and debris on public land, and long-term like potholes, unpaved roads and broken footpaths.
To evaluate the impact of the programme on the ground, 35 portable low-cost sensors were deployed after thorough calibration in Jahangirpuri, Rohini, and Karol Bagh, all of which already had an existing continuous ambient air quality monitoring station. The analysis is based on data on the 65 long-term issues that were resolved and which were within the vicinity of the sensors. IIT-D, which used data from the nearest continuous air monitoring stations and portable low-cost sensors, found a decline in PM2.5 levels in these three clusters, reducing by 26.6% in Jahangirpuri, 15.7% in Rohini and 15.3% in Karol Bagh.
Sagnik Dey, professor at the Centre for Atmospheric Sciences, IIT-D who led the study, said that for the first time, portable low-cost sensors had been effectively deployed to accurately quantify and demonstrate the potential impact of targeted interventions. “The substantial reductions in PM2.5 levels locally are promising and underscore the efficacy of this data-driven approach,” said Dey. “Our research provides robust evidence that addressing both short-term and long-term pollution sources can yield substantial and sustained improvements in air quality.”
Tariq Thomas, additional commissioner, MCD, said at an event in IIT-Delhi, “The study highlights the success of MCD and A-PAG’s collaborative efforts, showcasing how targeted interventions can lead to notable air quality improvements in the city.” He added, “MCD has implemented dust control measures, enhanced waste management systems and engaged with residents to create cleaner, healthier neighbourhoods.”