Japanese Tier-1 major Denso, which is a top component maker supplying a variety of parts, ranging from air-conditioning and thermal management systems to filters, horns and spark plugs, among others, to leading passenger vehicle, two-wheeler and commercial vehicle OEMs in India, is targeting robust growth in the future.
The company is targeting a CAGR of over 12% to more than double its FY2023 revenue of Rs 9,000 crore to Rs 20,000 crore by 2030. While Denso is betting big on the anticipated demand for its existing products — in line with the projected growth of the Indian economy and consequentially its vehicle market – it is also eyeing strong gains from its upcoming range of products, particularly in the areas of ADAS and electrification.
MULTI-PRONGED APPROACH TO ADDRESS ICE-TO-EV TRANSITION
At the recently-concluded Auto Expo 2025, the company showcased its future product roadmap with an elaborate display of components and technologies related to advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), data-driven solutions, and electrified propulsion systems.
In an exclusive interaction with Autocar Professional, Yasuhiro Ida, CEO, India Region, Denso, and Chairman and Managing Director, Denso International India, said, “We see all technologies – ICE, hybrid, and EVs – growing in the Indian market by 2035. This is one of the most attractive propositions that India offers, and therefore, we are currently focusing on the domestic market.”
According to Ida, the company is adopting a multi-pronged approach to pragmatically address the ICE-to-EV transition, and hence, is developing several manufacturing and product technologies, including inverters, motors, and generators for hybrids and BEVs. “We continue to develop technologies such as process automation to enhance the manufacturing output of our ICE offerings, and concurrently, we are developing new technologies for hybrids and EVs,” he added.
“Corresponding to the movement of our key customers such as Toyota and Suzuki towards EVs, we are promoting several activities and gearing for the new technologies which will be localised in India. For example, we are planning to manufacture inverters, motor-generator, and other EV parts in India,” Ida pointed out. The company is likely to commence production of its EV-specific parts in India around FY2027-28.
Besides its existing portfolio of automotive products, the company is betting big on software, ADAS, and EV components to enable it to realise its revenue target by the turn of the decade.
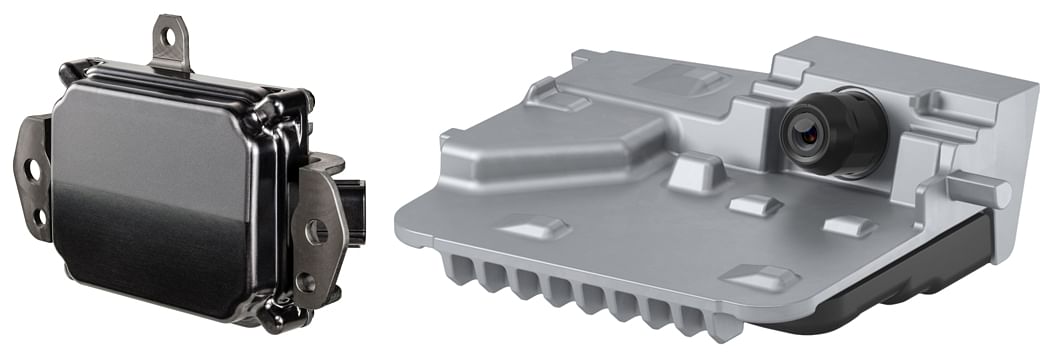
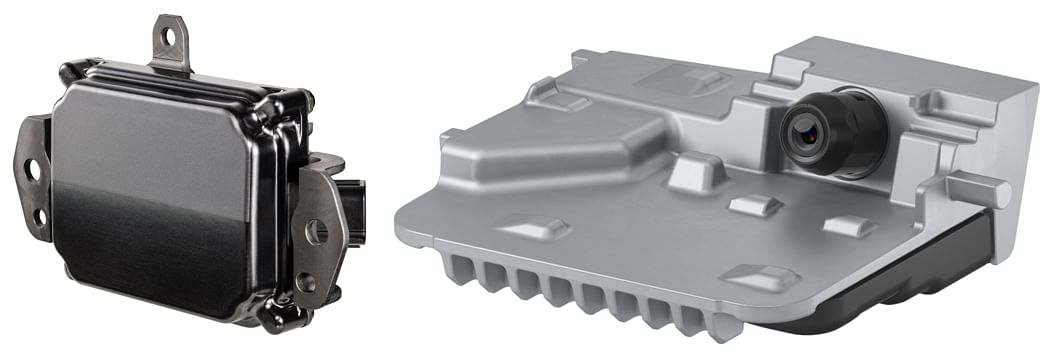 Above left: Denso’s millimetre-wave radar complements its vision sensors by gauging the appropriate distance with the vehicle in front to enable features such as Adaptive Cruise Control and Autonomous Emergency Braking.
Above left: Denso’s millimetre-wave radar complements its vision sensors by gauging the appropriate distance with the vehicle in front to enable features such as Adaptive Cruise Control and Autonomous Emergency Braking.
Above right: Denso vision sensors focus on object detection even in low-light conditions to ensure top-notch safety performance.
ADAS: A KEY PILLAR OF FUTURE GROWTH
For Denso, ADAS technology is one of the key pillars of its future growth roadmap in India. The company is also taking a holistic viewpoint of making a social impact by aiming to effectively reduce fatal road accidents in the country with its advanced solutions, customised for the local market.
“India is a unique market and our mission is to create India-centric solutions to reduce road accidents. Therefore, our strategy for ADAS is that we do not intend to simply extend the standard solutions meant for Japan, to India. Instead, we aim to develop ADAS technology which is suitable for the Indian road and traffic conditions,” Ida pointed out.
As a result, Denso is currently focusing on local R&D by collaborating with Indian universities as well as technology start-ups to offer ADAS solutions that perform reliably in Indian scenarios. While the company is already supplying the Level-2 ADAS modules on the Toyota Innova HyCross MPV, Denso envisions a regulatory push in the coming years acting as a key driver of volumes in this category.
As per Ida, “Regulations will be the big driver of ADAS demand from OEMs in India.” The company says that while it is currently focusing to support the voluntary plans of its OEM customers, such as Toyota Kirloskar Motor, the intensive market rollout of its ADAS offerings will follow the regulatory framework around the life-saving technology.
He also pointed out that Denso will explore ADAS opportunities beyond the Japanese OEMs present in India. The company aims to target the likes of Tata Motors and Mahindra & Mahindra which have already started offering ADAS features in their passenger vehicle models such as the Tata Curvv, Mahindra XUV700, Mahindra XEV9e, and BE 6, on sale in the country.
eAxle, jointly developed by BluE Nexus, Aisin and Denso, for the Suzuki e-Vitara. Production in India will contribute to the rollout of Suzuki BEVs around the world in line with market needs.
FOCUS ON LOCALISATION OF EV COMPONENTS
With growing demand for EVs and hybrids in India, Denso is optimistic about hybrids and EVs registering equal growth in the Indian passenger vehicle market over the next five years. However, the company expects the transition to fully-electric vehicles to accelerate only after 2035. Therefore, the company is developing small production systems to focus on small batches of EV components until demand takes off rapidly. Denso will commence local manufacturing of EV components in India around FY2027-28.
As a run up to local production, Denso is also contributing to strengthen the entire supply chain, particularly the Tier-3 and Tier-4 vendors, and gear them towards the localisation of EV technology, in line with the ‘Make-in-India’ vision of the Indian government. “Gradually, we must think about the supply chain management within the country. To do so, we need to first develop the small-volume manufacturing technology, and then scale as per the volume growth,” Ida explained.
With the core EV drivetrain – e-motors, generators, and inverters – being common to both propulsion systems, Denso is confident of serving the market with its advanced solutions. The Japanese Tier-1 major could also leverage these products for fuel-cell vehicles, if they gain traction in India in the future.
Given that OEMs such as Maruti Suzuki have outlined strategies to undertake export of electric vehicles from India to overseas markets such as Europe, and Japan, Denso says it will leverage its strength of ‘quality management’ going forward. “Improving quality further will be our endeavour as our customers in India are not only looking at the local market, but also at exports. Therefore, in future, more than cost, quality will be an essential parameter, and we will focus on attaining the right balance between cost and quality,” Ida highlighted.
Denso will focus on automation, automatic inspection systems, as well as effective Quality-Assurance networks that utilise IoT to bolster its quality promise with the commencement of localised electrification component supplies to OEMs in India in the next two years.
COLLABORATIVE APPROACH FOR SDVs
Another emerging trend that is increasingly making inroads in the automotive industry globally is that of the Software-Defined Vehicle or SDV. With software set to bring a complete overhaul of the vehicle Electrical and Electronics (E/E) architecture, it is set to play a crucial role in determining key vehicle functions as well as connectivity with the surrounding ecosystem.
Denso eyes SDV as a huge opportunity, and the company is bullish on the talent in India to drive software development for global application. While the Japanese Tier-1 major established a local R&D centre in India in 2012, with the increasing role of software and electronics in modern vehicle platforms, the company is expanding its local R&D capabilities.
To venture beyond mass-production support and application engineering in India, Denso aims to tap into the future technological trends by leveraging the talent available in the country. The company is recruiting high-quality resources from top-Tier engineering institutions in India, and is also collaborating with IT companies as well as start-ups to lead its software initiatives in the country. These partnerships will see the development of a common global software, as well as customisation of software for each market’s unique requirements.
To stay ahead of the curve, Denso is collaborating with technology start-ups such as those in Hyderabad’s T-Hub, as well as within the Nasscom umbrella, to explore the development of cutting-edge AI, ML, and IoT technologies of the future. “Our focus is to contribute to the India region. We are developing not just technology, but human resources as well, for which we are collaborating with start-ups as well as seeing strong collaboration between our R&D teams in India and Japan,” Ida said.
The company has also forayed into the area of data-driven services as an additional source of revenue, whilst targeting to make a societal impact. Through its ‘Solwer’ and ‘KaizenIoT’ platforms, it aims to leverage data science, image recognition, and AI, to offer interventions in areas such as transport and warehouse management, carbon-footprint management, and factory productivity optimisation. “We are expanding the use of our technology developed for in-car application, to outside the car, and solve social issues in India and other emerging markets,” he added.
ZEROING IN ON NET-ZERO EMISSIONS BY 2035
Denso has a global target to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2035, and the company has already switched to green energy at its manufacturing locations in India, while reusing waste, and deploying CO2-reduction technologies such as hydrogen die-casting systems as well. Its focus on automation will further enhance manufacturing efficiencies at its production sites in India.
With a strong legacy in automotive thermal management, which is also a key engineering frontier in electrified vehicles, Denso is confident to leverage its competency to emerge as not just a component supplier, but as one of the leading ‘systems’ supplier when it comes to electrification.
Strategically, India is a significant market for Denso globally, and when it comes to the development and introduction of new technologies such as ADAS, and software, India, with its robust talent and market dynamics, is set to play a big role for the Japanese giant in the coming years.