At some point in the future, while riding along in a car, a kid may ask their parent about a distant time in the past when people used steering wheels and pedals to control an automobile. Of course, the full realization of the “auto” part of the word — in the form of fully autonomous automobiles — is a long way off, but there are nonetheless companies trying to build that future today.
However, changing the face of transportation is a costly business, one that typically requires corporate backing or a lot of venture funding to realize such an ambitious goal. A recent funding round, some $128 million raised in a Series A round by Shenzhen-based Roadstar.ai, got us at Crunchbase News asking a question: Just how many independent, well-funded autonomous vehicles startups are out there?
In short, not as many as you’d think. To investigate further, we took a look at the set of independent companies in Crunchbase’s “autonomous vehicle” category that have raised $50 million or more in venture funding. After a little bit of hand filtering, we found that the companies mostly shook out into two broad categories: those working on sensor technologies, which are integral to any self-driving system, and more “full-stack” hardware and software companies, which incorporate sensors, machine-learned software models and control mechanics into more integrated autonomous systems.
Full-stack self-driving vehicle companies
Let’s start with full-stack companies first. The table below shows the set of independent full-stack autonomous vehicle companies operating in the market today, as well as their focus areas, headquarter’s location and the total amount of venture funding raised:
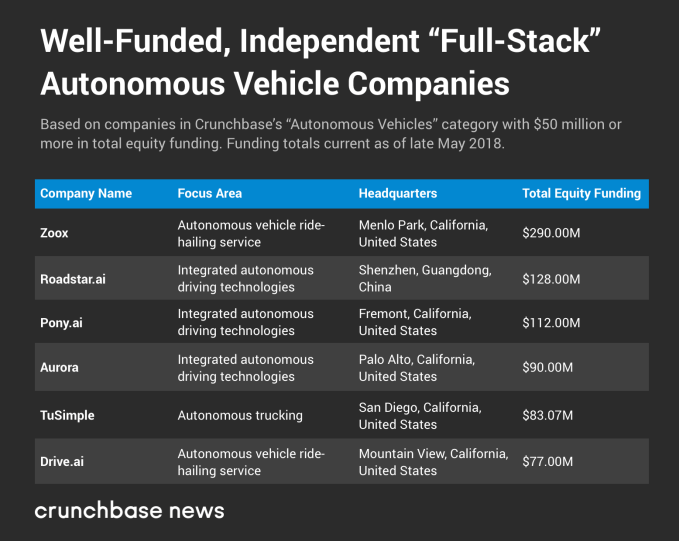
Note the breakdown in focus area between the companies listed above. In general, these companies are focused on building more generalized technology platforms — perhaps to sell or license to major automakers in the future — whereas others intend to own not just the autonomous car technology, but deploy it in a fleet of on-demand taxi and other transportation services.
Making the eyes and ears of autonomous vehicles
On the sensor side, there is also a trend, one that’s decidedly more concentrated on one area of focus, as you’ll be able to discern from the table below:
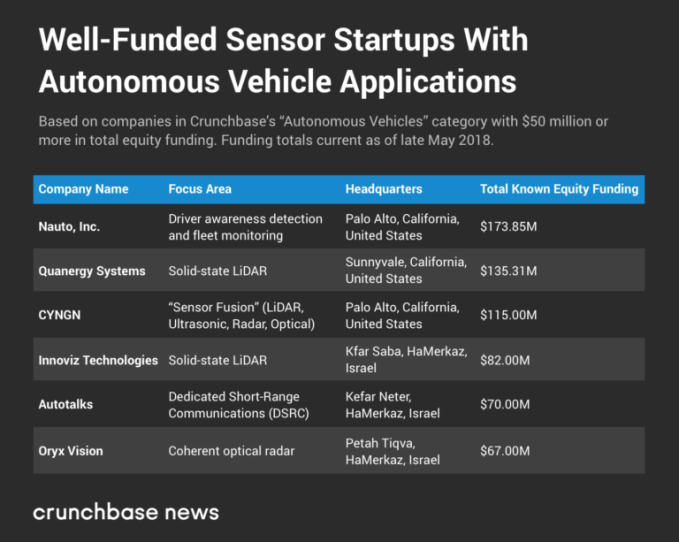
Some of the most well-funded startups in the sensing field are developing light detection and ranging (LiDAR) technologies, which basically serve as the depth-perceiving “eyes” of autonomous vehicle systems. CYNGN integrates a number of different sensors, LiDAR included, into its hardware arrays and software tools, which is one heck of a pivot for the mobile phone OS-maker formerly known as Cyanogen.
But there are other problem spaces for these sensor companies, including Nauto’s smart dashcam, which gathers location data and detects distracted driving, or Autotalks’s DSRC technology for vehicle-to-vehicle communication. (Back in April, Crunchbase News covered the $5 million Series A round closed by Comma, which released an open-source dashcam app.)
And unlike some of the full-stack providers mentioned earlier, many of these sensor companies have established vendor relationships with the automotive industry. Quanergy Systems, for example, counts components giant Delphi, luxury carmakers Jaguar and Mercedes-Benz and automakers like Hyundai and Renault-Nissan as partners and investors. Innoviz supplies its solid-state LiDAR technology to the BMW Group, according to its website.
Although radar and even LiDAR are old hat by now, there continues to be innovation in sensors. According to a profile of Oryx Vision’s technology in IEEE Spectrum, its “coherent optical radar” system is kind of like a hybrid of radar and LiDAR technology in that “it uses a laser to illuminate the road ahead [with infrared light], but like a radar it treats the reflected signal as a wave rather than a particle.” Its technology is able to deliver higher-resolution sensing over a longer distance than traditional radar or newer LiDAR technologies.
Can startups stack up against big corporate competitors?
There are plenty of autonomous vehicle initiatives backed by deep corporate pockets. There’s Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet, which is subsidized by the huge amount of search profit flung off by Google. Uber has an autonomous vehicles initiative too, although it has encountered a whole host of legal and safety issues, including holding the unfortunate distinction of being the first to kill a pedestrian earlier this year.
Tesla, too, has invested considerable resources into developing assistive technologies for its vehicles, but it too has encountered some roadblocks as its head of Autopilot (its in-house autonomy solution) left in April. The company also deals with a rash of safety concerns of its own. And although Apple’s self-driving car program has been less publicized than others, it continues to roll on in the background. Chinese companies like Baidu and Didi Chuxing have also launched fill-stack R&D facilities in Silicon Valley.
Traditional automakers have also jumped into the fray. Back in 2016, for the price of a cool $1 billion, General Motors folded Cruise Automation into its R&D efforts in a widely publicized buyout. And, not to be left behind, Ford acquired a majority stake in Argo AI, also for $1 billion.
That leaves us with a question: Do even the well-funded startups mentioned earlier stand a chance of either usurping market dominance from corporate incumbents or at least joining their ranks? Perhaps.
The reason why so much investor cash is going to these companies is because the market opportunity presented by autonomous vehicle technology is almost comically enormous. It’s not just a matter of the car market itself — projected to be over 80 million car sales globally in 2018 alone — but how we’ll spend all the time and mental bandwidth freed up by letting computers take the wheel. It’s no wonder that so many companies, and their backers, want even a tiny piece of that pie.