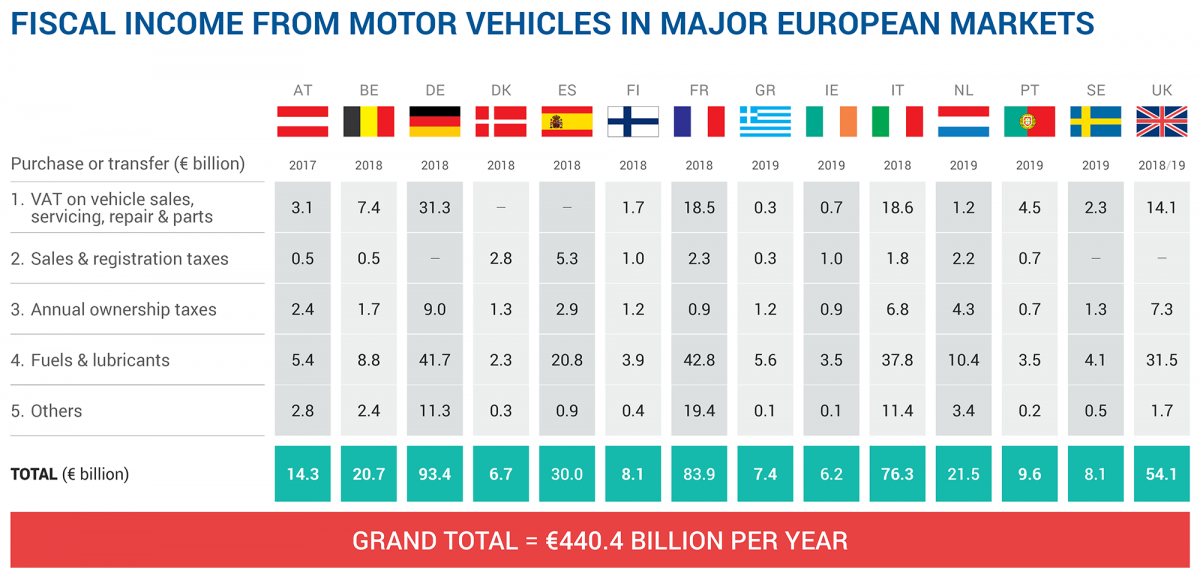
Brussels, 28 April 2020 – New data shows that motor vehicles generate more than €440 billion in taxation for national governments in the major EU markets plus the UK, the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) reports.
Motor tax revenues collected by governments have increased by almost 3% compared to the previous year, and the grand total of €440.4 billion is equivalent to more than two and a half times the total budget of the European Union.
“This just goes to show the sheer scale of the importance of the automobile industry to Europe,” stated Eric-Mark Huitema, ACEA Director General. “It is clearly paramount to the overall health of the EU economy, and government budgets in particular, that we can successfully re-launch our industry in the aftermath of the COVID-19 crisis.”
ACEA published this new data today in the 2020 edition of its Tax Guide, which compiles the latest information about taxes on vehicle acquisition (VAT, sales tax, registration tax), ownership (annual circulation tax, road tax) and motoring (fuel tax) in the EU and other key markets around the world.
The top 5 countries with the highest motor tax revenues are:
- Germany − €93.4 billion
- France − €83.9 billion
- Italy − €76.3 billion
- United Kingdom − €54.1 billion
- Spain − €30.0 billion
According to the new Guide, 24 countries levy car taxes partially or totally based on the CO2 emissions and/or fuel consumption of a vehicle. The three countries that do not apply CO2-based taxation are Estonia, Lithuania and Poland. Several countries still tax cars on their power, price, weight, cylinder capacity, or a combination of these factors.
The Tax Guide also shows that stimuli for electrically-chargeable cars are available in 24 out of the 27 EU states now. However, just 13 member states offer purchase incentives, such as bonus payments or premiums, to buyers of electric cars. Most countries grant only tax reductions or exemptions.
***
Notes for editors
- The full 2020 edition of the ACEA Tax Guide is available at:
- An interactive map showing fiscal income from motor vehicles in the major European markets can be found here:
- In this context, the major European markets are Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom. For other EU countries, data on motor tax revenues are not available.
- This Guide covers the 27 member states of the European Union, the United Kingdom and the three EFTA countries (Iceland, Norway and Switzerland). In addition, it also provides in-depth information for China, India, Japan, Korea, Russia, Turkey and the United States.
- ACEA’s statement, ‘Corona crisis: Towards a strong and green re-launch of the EU auto industry’, can be found here:
About ACEA
- ACEA represents the 16 major Europe-based car, van, truck and bus manufacturers: BMW Group, CNH Industrial, DAF Trucks, Daimler, Ferrari, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, Ford of Europe, Honda Motor Europe, Hyundai Motor Europe, Jaguar Land Rover, PSA Group, Renault Group, Toyota Motor Europe, Volkswagen Group, Volvo Cars, and Volvo Group.
- More information about ACEA can be found on www.acea.be or www.twitter.com/ACEA_eu.
- Contact: Cara McLaughlin, Communications Director, [email protected], +32 485 88 66 47.
About the EU automobile industry
- 13.8 million Europeans work in the auto industry (directly and indirectly), accounting for 6.1% of all EU jobs.
- 11.4% of EU manufacturing jobs – some 3.5 million – are in the automotive sector.
- The automobile industry generates a trade surplus of €84.4 billion for the EU.
- The turnover generated by the auto industry represents over 7% of EU GDP.
- Investing €57.4 billion in R&D annually, the automotive sector is Europe’s largest private contributor to innovation, accounting for 28% of total EU spending.